E-commerce Income Statements - A Guide to The Profit and Loss Statement

In the fast-paced realm of e-commerce, understanding the financial heartbeat of your business is critical. An e-commerce income statement, also known as a profit and loss or P&L statement, is a financial report showing the revenues, expenses, and profits of an online business over a specific period. It can help small businesses to track their performance, identify areas of improvement, and plan for the future.
Contents
Choosing Your Path: Methods for Preparing a Profit and Loss Statement
FAQs
Choosing Your Path: Methods for Preparing a Profit and Loss Statement
There are different methods for preparing a P&L statement or income statement, depending on the level of detail and accuracy you need. Some of the standard techniques are
Single-step Method
It is the most straightforward method, where you only need to subtract your total expenses from your total revenues to get your net income. This method does not separate your operating and non-operating activities, COGS, or other costs. It suits small businesses with simple transactions and few income and expense items.
Multi-step Method
It is a more detailed and comprehensive method, where you must separately calculate your gross profit, operating income, and net income. This method separates your operating and non-operating activities, COGS, and other expenses. It suits larger businesses with complex transactions and multiple income and expense items.
Cash Basis Method
It is a method where you only record your revenues and expenses when cash is received or paid. This method does not account for accruals, such as accounts receivable and payable, prepaid expenses, and deferred revenues. It suits businesses with minimal inventory and credit transactions and want to track their cash flow closely.
Accrual Basis Method
It is a method where you record your revenues and incurred expenses, regardless of when cash is received or paid. This method accounts for accruals, such as accounts receivable and payable, prepaid expenses, and deferred revenues. It suits businesses with significant inventory and credit transactions and wants to match their revenues and costs more accurately.
For e-commerce business owners, the best method for preparing a P&L statement or income statement depends on their business's size, complexity, and nature. However, some general guidelines are:
If you are a small or new e-commerce business, consider using the single-step or cash-based method, as they are easier to prepare and understand and require less data and adjustments.
Suppose you are a large or established e-commerce business. In that case, use the multi-step or accrual basis method to provide more accurate information and comply with accounting standards and tax regulations.
Note: Regardless of your chosen method, you should always make sure that your P&L statement or income statement is consistent, complete, and reliable. You should also review it regularly and compare it with your budget, goals, and industry benchmarks.
Decoding the Financial Narrative: How to Read a Profit and Loss Statement
The Profit and Loss Statement is essential for small business owners to track their company’s financial performance. Let’s explore what information is in a typical profit and loss statement and how to use it to make better business decisions.
Information Found on a Profit & Loss Statement
A typical profit and loss statement will include the following information:
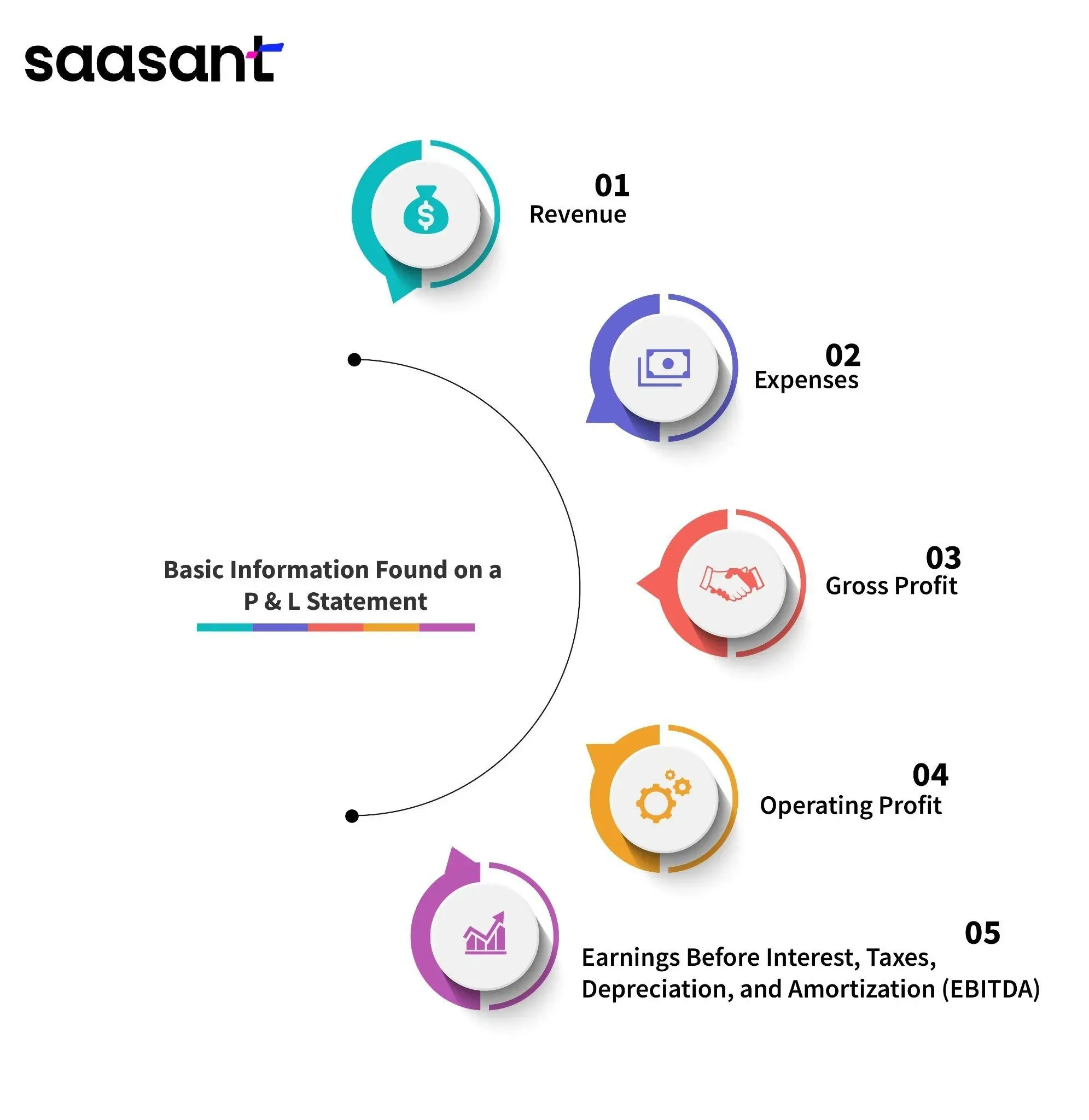
Revenue: This is the total amount the business earns from selling its products or services during a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It is also called sales or income.
Expenses: Expenses are the total business costs during the same period. They include the direct costs of producing or delivering the products or services, such as materials, labor, and shipping, and the indirect costs of operating the business, such as rent, utilities, marketing, and salaries.
Gross Profit: This is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), which are the direct costs of producing or delivering the products or services. It shows how much money the business makes from its core activities before deducting any operating expenses.
Operating Profit: This is the difference between gross profit and operating expenses, which are the indirect business costs. It shows how much money the business makes before accounting for interest, taxes, or non-operating income or expenses.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA): This is the operating profit plus depreciation and amortization, which are the non-cash expenses that reduce the value of the business’s assets over time. It shows how much cash the company generates from its operations before paying interest or taxes.
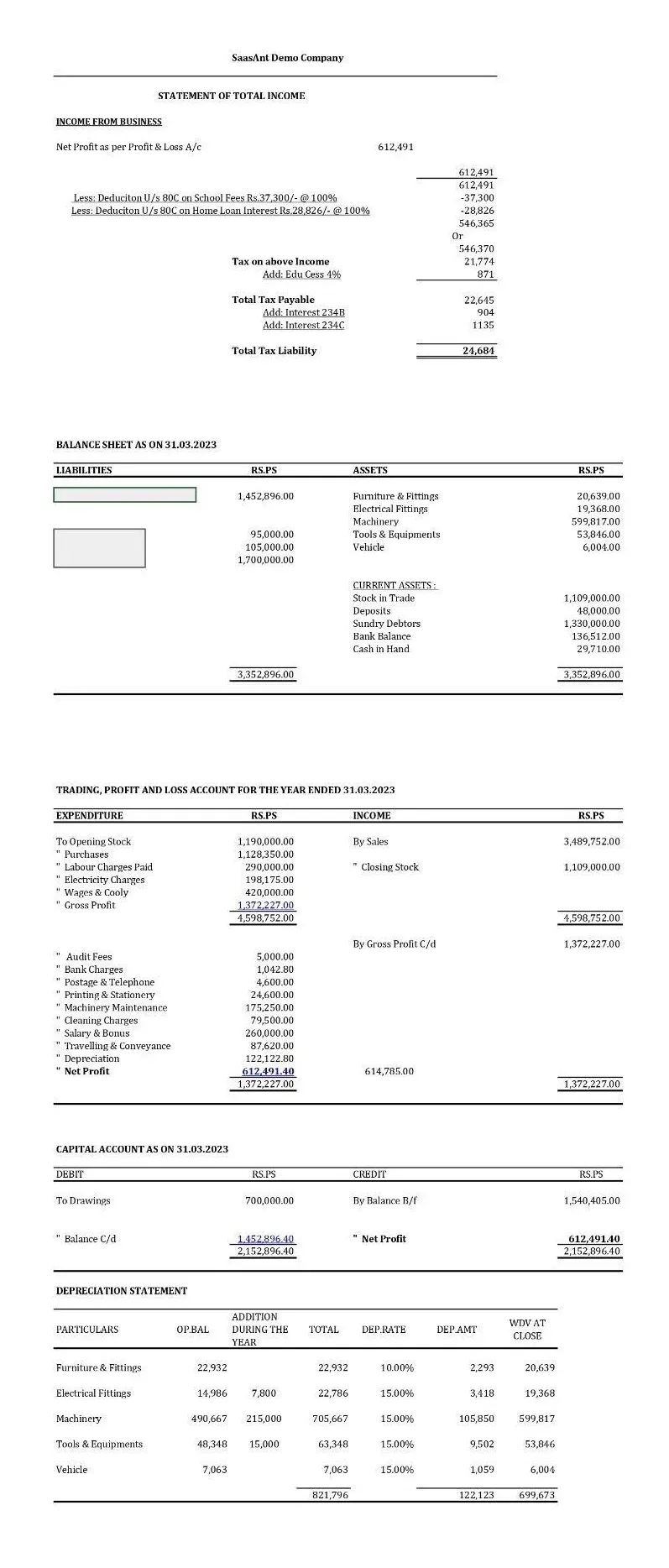
A simple Profit and Loss Statement:
 Bookkeeping software like QuickBooks can generate financial reports in a snap. But entering all the transactions, like income, expenses, and much more, into QuickBooks can be time-consuming. That’s why you need integrations like PayTraQer to import your data into QuickBooks in minutes.
Bookkeeping software like QuickBooks can generate financial reports in a snap. But entering all the transactions, like income, expenses, and much more, into QuickBooks can be time-consuming. That’s why you need integrations like PayTraQer to import your data into QuickBooks in minutes.
PayTraQer connects QuickBooks Online or Xero to your payment processors and e-commerce platforms, such as PayPal, Stripe, Square, Shopify, and Amazon. It syncs your transactions with accurate information, such as customers, sales, fees or expenses, taxes, refunds, and multi-currency. It also helps you reconcile your accounts quickly and prepare your P&L or income statement. Try PayTraQer for free today and see how it can simplify your accounting for your online business.
Balancing Act: Profit and Loss Statement vs. Balance Sheet
A profit and loss (profit and loss) statement summarizes a company's revenues, expenses, and profits/losses over a given period.
On the other hand, a balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific time.
So, what’s the difference between a profit and loss statement and a balance sheet?
Let’s take a closer look:
The main difference between a profit and loss statement and a balance sheet is that a profit and loss statement shows a company’s financial performance over time, while a balance sheet shows a company’s financial position at a specific time.
A profit and loss statement can track trends in revenue, expenses, and profits/losses over time. This information can help decide where to allocate resources and how to adjust pricing.
A balance sheet provides information about a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. This information can help assess a company’s financial health and determine whether it can meet its financial obligations.
Both profit and loss statements and balance sheets are essential tools for small business owners.
Profit and loss statements can help identify trends and inform pricing and resource allocation decisions.
Balance sheets can provide insights into a company’s financial health and help assess its ability to meet its obligations.
Empowering Your Business: Benefits & Advantages of Understanding the Profit and Loss Statement
When running a small business, one of the most important things you can do is keep a close eye on your finances. It includes understanding your profit and loss statement (profit and loss).
Your profit and loss is a crucial financial document that outlines your revenue, expenses, and profits for a specific period. It can help you track your progress, identify areas of opportunity, and make more informed decisions about where to invest your resources.
There are many benefits and advantages to understanding your profit and loss. Here are just a few:
It can help you track your progress and identify areas of improvement.
It can give you a better understanding of your costs and where you can save money.
It can help you assess your pricing strategy and determine whether or not you’re making a profit.
It can provide insights into seasonal trends or changes in customer demand.
It can help you plan for future growth by identifying potential investment areas.
Cracking the Code: How to Analyze the Data in a Profit and Loss Statement
Assuming you understand the profit and loss statement, analyzing the data within it can be daunting to small business owners. Where do you even start?
Here are five tips on how to analyze the data in your profit and loss statement:
Know Your Margins
It is essential to consider this in your profit and loss statement. Your gross margin is your total revenue minus the cost of goods sold, divided by total revenue. It will give you a good idea of how much profit you’re making on each sale. Ideally, you want a high gross margin (meaning you’re making much profit per sale).
Look at Your Operating Expenses
These are the costs of running your business, like rent, utilities, marketing, etc. Keeping these costs in check is essential because they can eat into your profits quickly.
Analyze Your Customer Acquisition Costs
This number is compared to the lifetime value of a customer to see if it’s worth it.
Comparing With Previous Statements
When reviewing your profit and loss statement year-over-year, compare similar periods (like month-over-month or quarter-over-quarter). It will give you a more accurate picture of your business’s growth or decline.
Look At The Big Picture
Don’t get too caught up in the details of each line item on the profit and loss statement. Instead, take a step back and look at the big picture, such as the gross profit margin, the operating profit margin, operating expenses, the net profit margin, and taxes. It will help you identify any trends or red flags that may be present.
Use Other Financial Statements To Supplement
To deepen your grasp of the profit and loss statement, go beyond its examination and assess your balance sheet and cash flow statement. The supplementary financial documents, such as schedules of accounts receivable, inventory, fixed assets, schedules of cost of goods sold, selling and administrative expenses, schedules of cash flows from operating, investing, or financing activities, schedules of changes in equity or retained earnings, and much more offer valuable insights into the overall performance of your business.
Thinking Beyond Tradition: Alternatives to Traditional Profit & Loss Statements
Not every business uses the traditional profit and loss statement. Some enterprises use alternatives like the cash flow statement or the Statement of Changes in Equity. These statements can give you a different perspective on your business’s financial health.
The cash flow statement shows how much cash is coming from your business. It can be helpful if you’re trying to manage your cash flow or are concerned about needing more money to cover your expenses. The Statement of Changes in Equity shows how your equity has changed over time. It can be helpful if you’re trying to understand your business’s value or considering selling it.
Understanding and keeping track of a Profit and loss Statement is vital for any company and can provide valuable insights into the financial performance of your business. With some effort, you can use these facts and figures to make informed decisions that will help drive your business forward. So, get started today and make sure you are on top of your Profit & Loss statement!
Wrap Up
Unveiling the financial narrative of your e-commerce venture is pivotal, and mastering the e-commerce income statement is your guide. Whether opting for a single-step or multi-step method, the chosen approach should align with the business's scale. Integrating applications like PayTraQer streamlines accounting, ensuring precision in managing online business finances.
The article's insights, from decoding profit and loss statements to practical tips on data analysis, empower entrepreneurs to navigate financial terrains adeptly. Alternatives like cash flow statements offer a comprehensive perspective. As you embark on this journey, keep a close eye on your profit and loss statement, the compass steering your business towards enduring success.
FAQs
What is a Profit and Loss Statement, and why is it crucial for understanding financial health?
A Profit and Loss Statement, commonly known as an income statement, is a financial document that outlines a company's revenues, expenses, and net income over a specific period. It is crucial as it provides a comprehensive snapshot of the company's operational efficiency and overall financial viability, offering valuable insights for stakeholders.
Can you explain the components of eCommerce P&L?
eCommerce P&L includes sales, fees, operating expenses, and marketing expenditures. These components contribute to the overall financial picture by offering a detailed breakdown of the company's revenue sources and the costs associated with running the platform.
Are there any specific tools or platforms for creating an income statement online, and how do they streamline the process for businesses?
Yes, various online tools, such as Protoolio and Wise, and accounting platforms, like QuickBooks and Xero, streamline creating an income statement online. These applications facilitate accurate data compilation and analysis, ensuring businesses generate dynamic and accessible income statements reflecting real-time financial changes.