Mastering Journal Entries in QuickBooks: A Guide for New Users
For new accounting professionals and business owners, understanding the nuances of QuickBooks can streamline financial operations significantly. Journal entries, pivotal for maintaining accurate records, are an essential feature in QuickBooks that enables businesses to manage financial events that aren't otherwise captured in standard transaction categories. This guide aims to assist beginners in mastering the art of journal entries for better financial management and reporting.
Why Journal Entries Are Crucial
Journal entries in QuickBooks are not just a fundamental accounting practice; they are essential for several reasons:
Accuracy: They help record unique transactions such as owner contributions or loan interest payments, which might not neatly fit into predefined expense or revenue categories.
Compliance: Journal entries help ensure that your business's financial records comply with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Insights: They provide a clearer picture of your financial health, presenting a comprehensive view of all monetary activities.
Understanding Types of Journal Entries
Grasping the various types of journal entries can enhance your recording accuracy:
1. Adjusting Entries
These are made at the end of an accounting period to adjust income and expense allocation accurately. Types include:
Accrued Expenses: Expenses incurred but not paid (like unpaid utility bills).
Deferred Revenue: Payments received for services or goods not yet delivered.
Prepaid Expenses: Payments made for services or goods before they are received.
Depreciation: Allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life.
2. Reversing Entries
These are made at the beginning of a new accounting period, reversing specific adjusting entries from the previous period, which simplifies the new period's accounting.
3. Recurring Entries
Used for transactions that occur regularly, these entries automate the recording process, saving time and reducing potential errors.
4. Opening Balance Entries
Important when starting with QuickBooks or switching from another accounting system, these entries ensure your accounts start with the correct balances.
Creating Journal Entries in QuickBooks
QuickBooks simplifies the creation of journal entries:
QuickBooks Online
Navigate to "Accounting" > "Chart of Accounts."
Click "New," then select "Journal Entry."
QuickBooks Desktop
Go to the "Company" menu.
Choose "Make General Journal Entries."
Key Elements to Include in Journal Entries:
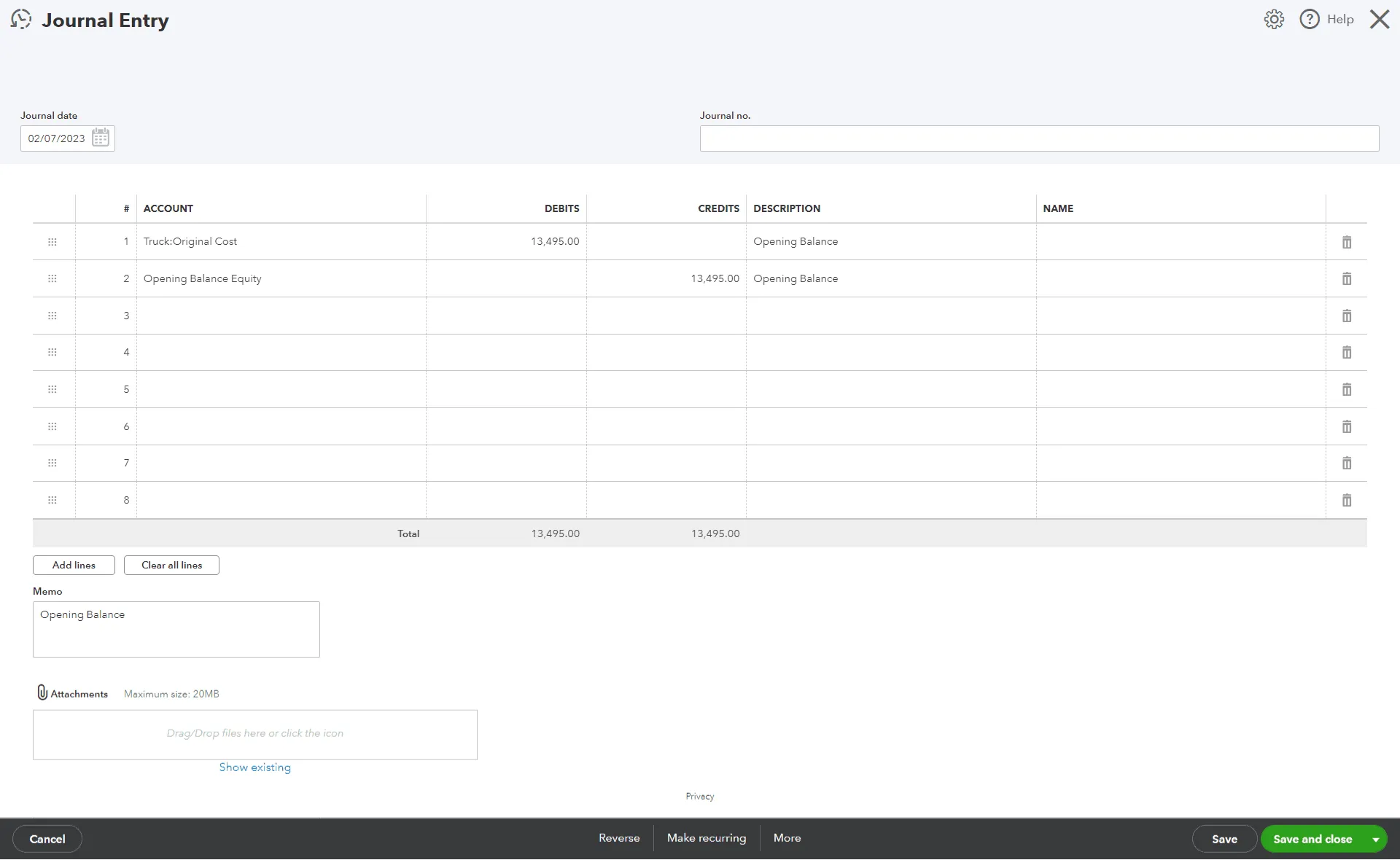
Date: The date of the transaction.
Entry Number: Automatically generated by QuickBooks.
Accounts Affected: Identify and select the accounts to debit and credit.
Amounts: Input the corresponding debit and credit values.
Memo: Add a brief note for context.
Always review your entries to ensure their accuracy before saving.
Managing Journal Entries
Viewing and Editing Entries
General Journal Report: This can be accessed via the "Reports" menu, allowing customization of date ranges and filters.
Direct Access: Locate entries using the "Chart of Accounts" or the search feature.
Editing Procedures
Locate the desired entry.
Modify the date, amount, or accounts as necessary.
Save the changes.
Correcting Errors
Simple Edits: Directly amend minor errors in the journal entry.
Reverse and Recreate: For significant errors affecting past periods, reverse the original entry and create a new one with the correct information. Consult with an accountant when necessary to avoid impacting financial reports.
Leveraging Technology: SaasAnt Transactions
SaasAnt Transactions enhances QuickBooks by facilitating the import and export of journal entry data:
Streamlined Imports: Import bulk journal entry data effortlessly, reducing manual entries and errors.
Simplified Exports: Export data in user-preferred formats for further analysis or reporting.
Practical Examples
Payroll: Debit Payroll Expenses, Credit Payroll Liabilities.
Depreciation: Debit Depreciation Expense, Credit Accumulated Depreciation.
Inventory Adjustment: Debit Inventory Asset, Credit Cost of Goods Sold.
Bad Debt Write-Off: Debit Bad Debt Expense, Credit Accounts Receivable.
Bank Reconciliation: Adjust the Cash account and other relevant accounts as necessary.
Conclusion
By mastering journal entries in QuickBooks, new users can enhance their accounting accuracy and gain deeper insights into their business finances. The integration of tools like SaaSant Transactions can further streamline and optimize financial management practices, making QuickBooks an even more powerful tool for business accounting.