Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor: Key Differences and How to Choose the Right Solution
 In the contemporary digital economy, e-commerce has become pivotal, driving significant transformations in how businesses operate and engage with customers. A critical component of this digital marketplace is the seamless and secure handling of online transactions. Understanding the intricacies of payment gateways and payment processors is essential to achieve this. This knowledge enhances the efficiency of financial transactions and ensures the security and trustworthiness of the e-commerce platforms.
In the contemporary digital economy, e-commerce has become pivotal, driving significant transformations in how businesses operate and engage with customers. A critical component of this digital marketplace is the seamless and secure handling of online transactions. Understanding the intricacies of payment gateways and payment processors is essential to achieve this. This knowledge enhances the efficiency of financial transactions and ensures the security and trustworthiness of the e-commerce platforms.
Contents
Brief Introduction to the Importance of Understanding Payment Gateways and Payment Processors
What is a Payment Gateway?
What is a Payment Processor?
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor: Key Differences
The Importance of Both in the Payment Ecosystem: Why Are Payment Gateways and Payment Processors Essential for Seamless Transactions?
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business?
Comparing Features and Benefits of Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Considering Costs and Fees of Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Best Practices for Using Payment Gateways and Processors: Tips and Best Practices for Maximizing Efficiency
Common Challenges and Solutions While Using Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
FAQs
Brief Introduction to the Importance of Understanding Payment Gateways and Payment Processors
Payment gateways and payment processors form the backbone of online transactions, serving as the intermediaries between customers and merchants. A payment gateway is a technology merchants use to accept customer debit or credit card purchases. On the other hand, a payment processor is a service that handles the transactions between the merchant and the customer’s bank.
Understanding these elements is crucial for several reasons:
Security: Ensuring secure transactions is paramount in gaining and maintaining customer trust. Payment gateways and processors implement security measures to protect sensitive data, including encryption and fraud detection.
Efficiency: Efficient payment processing can significantly enhance the customer experience by reducing transaction times and minimizing errors.
Global Reach: For businesses aiming to operate internationally, it is vital to understand and integrate various payment gateways and processors that cater to different regions.
Cost Management: Different payment gateways and processors have varied fee structures. A thorough understanding enables businesses to choose the most cost-effective options, improving their bottom line.
Compliance: Adhering to financial regulations and standards, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), is mandatory. Knowledge of payment gateways and processors helps businesses stay compliant with these regulations.
In conclusion, grasping the nuances of payment gateways and processors is indispensable for any business looking to thrive in e-commerce. This understanding facilitates secure and efficient transactions and is crucial in expanding a business’s global reach and ensuring regulatory compliance.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a critical technology that facilitates online transactions between customers and merchants. It acts as an intermediary, ensuring the transaction data is securely transmitted from the customer to the merchant and then to the payment processor.
A payment gateway is a service that authorizes and processes payments for online and brick-and-mortar businesses. It encrypts sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, ensuring that the data passed between the customer, the merchant, and the payment processor remains secure.
Transaction Authorization
When a customer initiates a purchase, the payment gateway validates the transaction details, ensuring that sufficient funds are available and that the payment method is legitimate. This involves verifying the customer's credit card information and checking for potential fraud.
Data Encryption
One of the primary functions of a payment gateway is to secure transaction data. It uses encryption protocols to protect sensitive information, such as credit card numbers and personal details, from being intercepted by unauthorized parties.
Communication with Payment Processors
After authorizing the transaction, the payment gateway forwards the payment details to the payment processor, which communicates with the customer’s bank to complete the transaction. This seamless communication is crucial for the timely processing of payments.
Transaction Completion
Once the payment processor confirms the transaction, the payment gateway sends a confirmation message to the merchant and the customer. This message typically includes transaction status, receipt number, and relevant order information.
Key Features
Security Protocols: Payment gateways employ various security measures, including SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption, tokenization, and compliance with PCI DSS standards to ensure the safety of transaction data.
Multi-Currency Support: Payment gateways support multiple currencies for international businesses, facilitating cross-border transactions.
Integration Capabilities: Modern payment gateways can be easily integrated with various e-commerce platforms, shopping carts, and accounting software, enhancing the overall functionality and user experience.
Benefits for Businesses
Enhanced Security: Payment gateways help businesses build trust with their customers by ensuring that all transaction data is encrypted and secure.
Improved Efficiency: Automated transaction processing reduces the time and effort required to handle payments manually, allowing businesses to focus on other critical operations.
Broader Payment Options: Payment gateways support various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers, offering customers greater flexibility.
In summary, a payment gateway is essential for any online business. It provides a secure, efficient, and versatile means of handling payments, contributing to a positive customer experience, and fostering business growth in the digital marketplace.
What is a Payment Processor?
In the ecosystem of online transactions, payment processors play an indispensable role, ensuring the seamless movement of funds between customers and merchants. A payment processor is a company or service that handles transactions from various payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, and digital wallets, ensuring that payments are transferred securely and efficiently.
A payment processor is a service provider that manages transactions between a merchant and a financial institution. It acts as a mediator, facilitating the transfer of funds from the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s account and ensuring the payment process is completed accurately and securely.
Transaction Facilitation
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment processor is responsible for transmitting the payment information from the merchant to the customer’s issuing bank and obtaining authorization for the transaction. This involves verifying the payment details and ensuring the customer has sufficient funds or credit.
Settlement of Funds
After the transaction is authorized, the payment processor manages the settlement process, which involves transferring the funds from the customer's bank to the merchant's bank. This process ensures that the merchant receives the payment for the goods or services sold.
Risk Management
Payment processors implement various measures to mitigate risks associated with fraudulent transactions. This includes monitoring transactions for suspicious activities, employing encryption protocols, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as PCI DSS.
Chargeback Handling
When a customer disputes a transaction, the payment processor manages the chargeback process. This involves investigating the dispute, facilitating communication between the merchant and the customer, and ensuring the issue is resolved per the payment network’s rules.
Key Features
Fraud Prevention: Payment processors utilize advanced fraud detection tools and techniques to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, safeguarding merchants and customers.
Speed and Efficiency: Modern payment processors are designed to handle transactions quickly and efficiently, reducing merchants' time to receive their funds.
Compliance and Security: By adhering to industry standards and regulatory requirements, payment processors ensure that all transactions are conducted securely and comply with relevant laws.
Benefits for Businesses
Streamlined Payment Operations: Payment processors automate the complex process of handling transactions, reducing businesses' manual workload and allowing them to focus on core activities.
Enhanced Security: With robust security measures, payment processors help protect businesses from fraud and data breaches, fostering customer trust.
Global Reach: Payment processors support various payment methods and currencies, enabling businesses to expand their reach to international markets and cater to a diverse customer base.
In conclusion, payment processors are vital to the e-commerce infrastructure, ensuring transactions are processed smoothly and securely. By understanding their role and benefits, businesses can optimize payment operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve greater financial efficiency in the competitive digital marketplace.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor: Key Differences
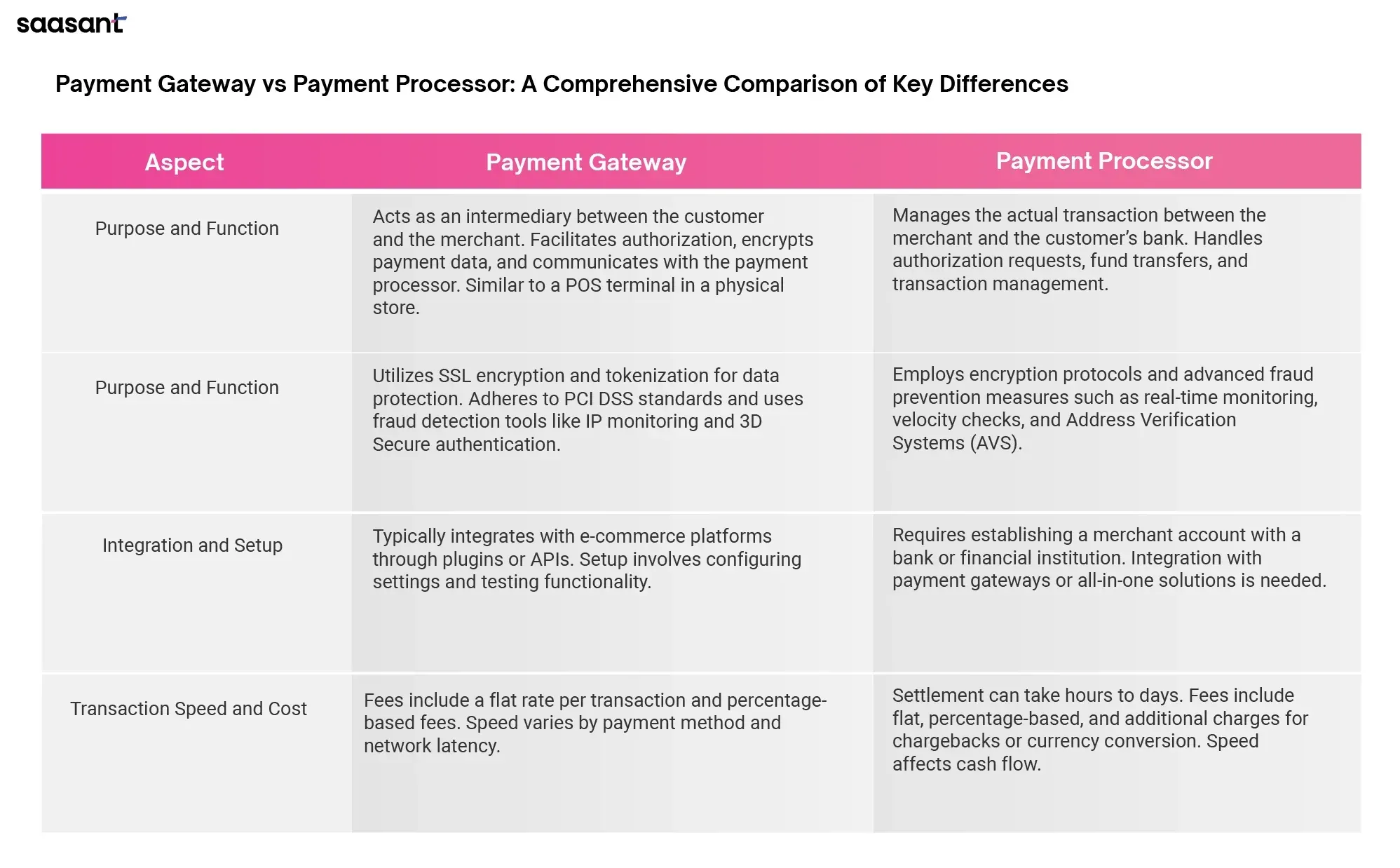
Purpose and Function
Payment Gateway
A payment gateway primarily acts as an intermediary between the customer and the merchant, facilitating the initial phase of an online transaction. Its main functions include authorizing transactions, encrypting sensitive payment data, and facilitating communication with the payment processor. When a customer initiates a purchase, the payment gateway ensures that the payment information entered is securely transmitted and validated before the transaction proceeds. It is the digital equivalent of a physical store's point-of-sale (POS) terminal. The gateway is responsible for communicating transaction information to the payment processor or acquiring bank, ensuring that the transaction details are correct and sufficient funds are available in the customer’s account.
Payment Processor
A payment processor, in contrast, is responsible for managing the actual transaction between the merchant and the customer's bank. Its functions include handling the authorization requests from the payment gateway, settling the funds by transferring them from the customer's bank to the merchant's account and managing chargebacks and refunds. The payment processor is tasked with the seamless transfer of funds and the overall management of the transaction process. It works behind the scenes to ensure the transaction is completed, moving the money from the customer’s issuing bank to the merchant’s acquiring bank. This process includes several steps, such as verifying the transaction details, checking for fraud, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
Security and Fraud Prevention
Payment Gateway
Security is a paramount concern in online transactions, and payment gateways are equipped with robust measures to protect sensitive payment data. These measures include SSL encryption, which secures the data transmitted between the customer and the merchant. Tokenization replaces sensitive payment information with unique tokens that can only be interpreted by the payment processor. Compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) ensures that the gateway meets the highest security standards. Payment gateways also use fraud detection tools to identify and prevent suspicious activities. These tools can monitor IP addresses, track transaction patterns, and implement 3D Secure authentication, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring the customer to enter an additional password or code during the transaction.
Payment Processor
Payment processors focus on the secure handling of transaction data and funds. They utilize encryption protocols to protect data during transmission and storage. Payment processors also implement advanced fraud prevention measures, such as real-time transaction monitoring, which helps detect and prevent fraudulent transactions as they occur. Velocity checks limit the number of transactions processed within a specific timeframe, reducing the risk of fraud. Address Verification Systems (AVS) compare the billing address provided by the customer with the address on file with the credit card issuer. These security measures ensure that the funds are securely transferred and that fraudulent transactions are detected and mitigated.
Integration and Setup
Payment Gateway
Integrating a payment gateway with an e-commerce platform or website is typically straightforward and user-friendly. Most payment gateways offer plugins or APIs that can be easily integrated into popular e-commerce platforms, such as Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento. The setup process usually involves creating a merchant account, configuring the payment gateway settings, and testing the integration to ensure seamless functionality. Detailed documentation and support are often provided to guide merchants through the process. Once integrated, the payment gateway allows businesses to start accepting online payments quickly, enhancing the overall customer experience by providing a secure and efficient checkout process.
Payment Processor
Setting up a payment processor may require more effort, as it involves establishing a merchant account with a bank or financial institution. This process includes submitting business and financial information, undergoing a credit check, and signing a merchant agreement.
The approval process can take several days, depending on the bank's requirements and the complexity of the business's financial structure. Once the merchant account is approved, the payment processor can be integrated with the payment gateway to facilitate transactions. Some payment processors offer all-in-one solutions, including the gateway and processing services, simplifying the setup process.
These integrated solutions can streamline the transaction process and reduce the need for multiple vendors.
Transaction Speed and Cost
Payment Gateway
Payment gateways typically process transactions in real-time or near real-time, ensuring quick authorization and confirmation. Transaction processing speed can vary based on network latency, the complexity of fraud detection algorithms, and the payment method used.
For example, credit card transactions may be processed faster than bank transfers, which can take longer to clear. In terms of cost, payment gateways charge fees for each transaction. These fees can include a flat fee per transaction, a percentage of the transaction amount, and additional fees for specific payment methods or services.
Merchants must carefully evaluate the fee structures of different payment gateways to choose the most cost-effective option for their business.
Payment Processor
Payment processors are responsible for the actual settlement of funds, which can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the bank's processing times and the type of transaction.
The speed of settlement can impact the overall cash flow for the merchant, affecting their ability to manage inventory and operations. Payment processors also charge fees for their services, including flat fees, percentage-based fees, and additional charges for chargebacks, refunds, or currency conversion.
Merchants must understand these costs and factor them into their pricing strategies to maintain profitability. Businesses can optimize their cash flow and reduce transaction costs by selecting a payment processor with competitive fees and efficient settlement times.
The Importance of Both in the Payment Ecosystem: Why Are Payment Gateways and Payment Processors Essential for Seamless Transactions?
Payment gateways and processors are two pivotal components that ensure smooth transaction flow. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct yet complementary functions within the payment ecosystem. Understanding the significance of both elements can help businesses streamline their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive growth.
Payment Gateways: The Digital Front Door
A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates online transactions between the customer and the merchant. Acting as a digital front door, it plays a crucial role in ensuring the transaction process is smooth, secure, and user-friendly. Here’s a closer look at its primary functions:
Encryption: A payment gateway's foremost responsibility is protecting sensitive information. It encrypts sensitive data, such as credit card details, into a secure code during transmission. This encryption ensures that data remains confidential and protected from cyber threats.
Authorization: Before a transaction can proceed, the payment gateway verifies the customer's payment method. This involves checking whether the credit or debit card is valid and whether the account has sufficient funds. This step is crucial for preventing declined transactions and potential fraud.
Integration: Payment gateways are designed to integrate seamlessly with various e-commerce platforms, shopping carts, and mobile applications. This integration provides customers with a smooth and consistent checkout experience, reducing the likelihood of cart abandonment.
Fraud Detection: Advanced payment gateways employ sophisticated algorithms and machine-learning techniques to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions. They analyze transaction patterns, flagging suspicious activities and safeguarding the merchant and the customer from fraud.
Payment Processors: The Behind-the-Scenes Engine
While the payment gateway manages the customer-facing side of the transaction, the payment processor works behind the scenes to ensure that funds are transferred accurately and efficiently. The payment processor's primary responsibilities include:
Transaction Processing: Once the payment gateway has authorized the transaction, the payment processor takes over. It transmits the transaction details from the payment gateway to the appropriate banks and card networks for approval. This process involves communicating with the customer’s bank to confirm the availability of funds and with the merchant’s bank to facilitate the transfer.
Settlement: After the transaction is approved, the payment processor ensures that funds are transferred from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s account. This settlement process is vital for completing the transaction cycle and ensuring merchants receive their payments promptly.
Compliance: Payment processors are responsible for adhering to regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). Compliance with these standards ensures the secure handling of payment data, protecting against data breaches and financial losses.
Chargeback Management: When customers dispute a transaction, the payment processor assists merchants in managing chargebacks and resolving disputes. Effective chargeback management is essential for minimizing potential revenue losses and maintaining a positive customer relationship.
The Synergy: Creating a Seamless Payment Experience
The synergy between payment gateways and processors is fundamental to a seamless payment experience. Here’s why their collaboration is crucial:
Enhanced Security: The combined efforts of payment gateways and processors provide robust security for online transactions. While the gateway focuses on encryption and fraud detection, the processor ensures compliance with regulatory standards, creating a multi-layered security framework.
Efficient Transactions: The collaboration between gateways and processors results in swift and efficient transactions. The gateway handles the initial authorization and fraud detection, while the processor manages the back-end transaction processing and settlement, ensuring a smooth flow of funds.
Customer Trust: A seamless and secure payment experience is vital for building and maintaining customer trust. When customers feel confident that their transactions are safe and their data is protected, they are more likely to complete purchases and return for future transactions.
Scalability: The combined capabilities of payment gateways and processors enable businesses to scale their operations effectively. As transaction volumes increase, the integrated system can handle higher loads without compromising security or speed, supporting business growth.
Integrating payment gateways and processors is essential for any business seeking a seamless, secure, and efficient payment experience. By understanding these components' distinct yet complementary roles, companies can optimize their payment processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive growth. In a world where digital transactions are becoming increasingly prevalent, leveraging the strengths of both payment gateways and processors is the key to success in the digital marketplace.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business?
Choosing the right payment solution is a pivotal decision that can significantly influence your business’s efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall success. Given the vast array of payment solutions available, evaluating your specific needs is essential to find the best fit. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to assessing your business requirements and selecting the most suitable payment solution.

Assessing Your Business Needs
Before diving into the selection process, it's crucial to understand your business needs thoroughly. Here’s a detailed approach to help you determine what your business requires:
Analyze Your Business Model
Understanding your business model helps in identifying the most appropriate payment solution. Consider the following aspects:
Type of Business: Different business models have different requirements. For instance, an e-commerce store will need a robust online payment solution, while a physical retail store might prioritize point-of-sale (POS) systems. Subscription-based businesses may require recurring billing capabilities, while service-based businesses might need invoicing solutions.
Sales Channels: Determine through which channels you conduct transactions. If you operate online and offline, you need a payment solution that integrates seamlessly across all platforms. Multi-channel businesses often benefit from omnichannel payment solutions that unify payment processing across websites, mobile apps, and physical locations.
Transaction Volume: Assess your average transaction volume and size. High-volume businesses might prioritize solutions with lower transaction fees to reduce overall costs. In contrast, those with high-value transactions may focus more on advanced security features to protect large sums of money.
Identify Your Customer Base
Your customer base’s characteristics significantly influence your choice of payment solution. Consider the following factors:
Geographic Reach: Determine whether your business operates domestically, internationally, or both. A global audience requires a payment solution that supports multiple currencies and international payment methods. Solutions with global capabilities can facilitate smoother transactions for international customers and reduce conversion costs.
Payment Preferences: Analyze what payment methods your customers prefer. This could include credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets (such as PayPal, Apple Pay, or Google Wallet), bank transfers, or alternative payment methods like cryptocurrencies. Offering various payment options can enhance the customer experience and reduce cart abandonment.
Device Usage: Understand the devices your customers use to make purchases. If mobile transactions are prevalent, ensure the payment solution provides a seamless mobile experience. Responsive design and mobile optimization are critical for accommodating mobile users and enhancing their transaction experience.
Evaluate Security Requirements
Security is a critical factor in payment processing. A secure payment solution helps protect your business and customers from fraud and data breaches. Consider these aspects:
Compliance: Ensure the payment solution complies with industry standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). Compliance ensures the solution adheres to best practices for securing payment data and helps prevent breaches.
Fraud Prevention: Look for solutions that offer advanced fraud detection and prevention features. These can include real-time monitoring, machine learning algorithms, and fraud analytics. Effective fraud prevention minimizes the risk of unauthorized transactions and protects your business from financial losses.
Data Protection: Verify that the payment solution employs robust data protection measures. This includes encryption of sensitive information, tokenization to protect card details, and secure data storage practices. Protecting customer data is essential for maintaining trust and avoiding potential legal issues.
Assess Integration Capabilities
Seamless integration with your existing systems can streamline operations and enhance efficiency. Evaluate the following integration aspects:
E-commerce Platforms: If you run an online store, ensure the payment solution integrates smoothly with your e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento). This integration facilitates a streamlined checkout process and minimizes manual data entry.
Accounting Software: Integration with accounting software, such as QuickBooks or Xero, can automate financial record-keeping and reconciliation. This helps maintain accurate financial records and simplifies cash flow management.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Integrating with the payment solution can enhance customer relationship management for businesses using CRM systems. It allows you to track payment histories, manage customer interactions, and analyze transaction data to improve customer engagement.
Consider Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, your payment needs may evolve. Choose a solution that offers scalability and flexibility:
Scalability: Ensure the payment solution can handle increased transaction volumes as your business expands. A scalable solution can accommodate growth without compromising performance or requiring a complete overhaul of your payment systems.
Customizability: Opt for a solution that allows customization to meet your business needs. This includes customizable payment forms, flexible pricing models, and configurable settings. A customizable solution can adapt to changing business requirements and provide a tailored payment experience.
Selecting the proper payment solution involves thoroughly assessing your business model, customer base, security requirements, integration needs, and scalability. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can identify a payment solution that aligns with your business objectives, enhances customer satisfaction, and supports growth. In a rapidly evolving digital marketplace, choosing the right payment solution is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business’s success and operational efficiency.
Comparing Features and Benefits of Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Choosing the right payment solution ensures smooth transactions, customer satisfaction, and business growth. Payment gateways and processors are essential components in the payment ecosystem, offering unique features and benefits. This detailed comparison will help you understand their roles and how they can contribute to your business's success.
Key Features of Payment Gateways
Transaction Security
Encryption: Payment gateways use advanced encryption methods to secure sensitive information during transmission, protecting customer data from cyber threats.
Tokenization: Payment gateways minimize the risk of data breaches by replacing sensitive card details with unique tokens. Tokenization ensures that actual card information is not stored or transmitted during transactions.
Fraud Detection: Many payment gateways offer sophisticated fraud detection tools that use machine learning and real-time analytics to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions. These tools can detect unusual transaction patterns and flag potentially fraudulent activity.
Payment Method Support
Multiple Payment Methods: Payment gateways support various payment methods, including major credit and debit cards, digital wallets (e.g., PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Wallet), and alternative payment options like cryptocurrencies. This flexibility allows customers to choose their preferred payment method.
Multi-Currency Support: For businesses with an international customer base, payment gateways that support multiple currencies are essential. They facilitate transactions in different currencies, making it easier for global customers to complete their purchases without worrying about currency conversion issues.
User Experience
Seamless Checkout: Payment gateways provide a smooth and intuitive checkout process that reduces cart abandonment rates. Features like one-click payments and guest checkout options can enhance the customer experience.
Mobile Optimization: With the increasing use of mobile devices for online shopping, payment gateways must offer a mobile-optimized payment experience. This includes responsive design, mobile-friendly interfaces, and support for mobile wallets.
Customizable Payment Pages: Many payment gateways allow businesses to customize their payment pages to match their branding, providing customers with a consistent and professional look and feel.
Integration Capabilities
E-commerce Platforms: Payment gateways integrate seamlessly with popular e-commerce platforms such as Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, and BigCommerce. This ensures that businesses can quickly set up and start accepting payments online.
APIs and Plugins: For businesses with custom-built websites or applications, payment gateways offer APIs and plugins that facilitate easy integration. This allows businesses to tailor the payment process to their specific needs.
Key Features of Payment Processors
Transaction Handling
Authorization: Payment processors are crucial in authorizing transactions by verifying the customer's payment details with their issuing bank. This step ensures that the customer has sufficient funds and that the transaction is legitimate.
Settlement: Payment processors handle the settlement of funds, transferring money from the customer's bank to the merchant's account. This process involves multiple financial institutions and ensures that funds are accurately and promptly delivered.
Chargebacks: Payment processors are critical in managing chargebacks. They handle disputes and refunds, ensuring that merchants and customers are treated fairly during the resolution process.
Speed and Reliability
Swift Processing: Payment processors are known for processing transactions quickly. This ensures that customers receive confirmation of their purchases promptly, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
High Uptime: Reliable payment processors offer high uptime rates, minimizing the risk of downtime that could disrupt transactions. This reliability is crucial for maintaining customer trust and satisfaction.
Reporting and Analytics
Transaction Reports: Detailed transaction reports provide businesses valuable insights into their sales performance. These reports include information on successful payments, refunds, and chargebacks.
Sales Analytics: Payment processors offer sales analytics tools that help businesses identify trends, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make data-driven decisions. This information can be used to optimize marketing strategies and improve overall business performance.
Benefits of Payment Gateways
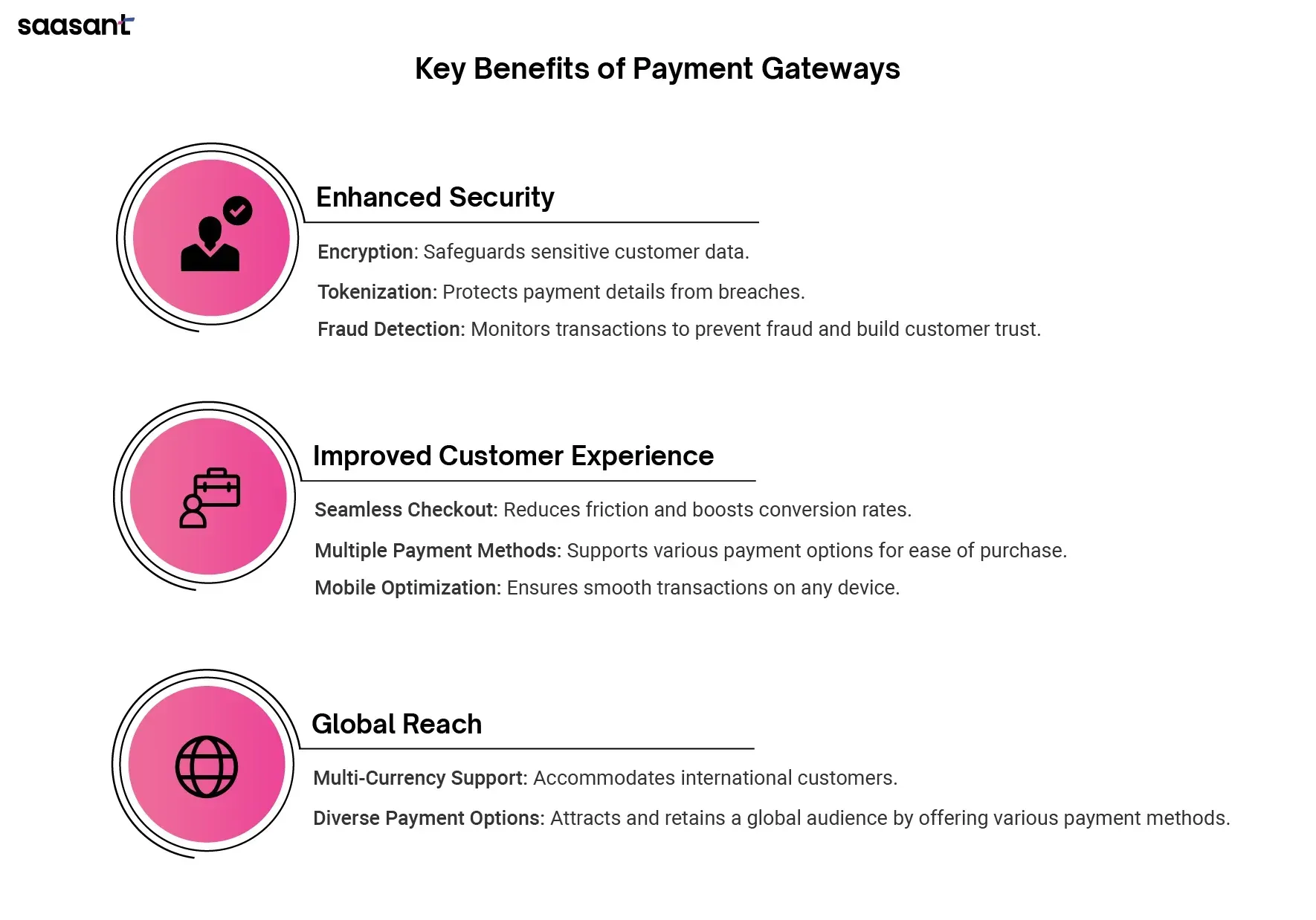
Enhanced Security
Payment gateways provide robust security features that protect sensitive customer data. Encryption and tokenization reduce the risk of data breaches, while fraud detection tools help prevent fraudulent transactions. These security measures build customer trust and protect your business from potential financial losses.
Improved Customer Experience
A seamless and intuitive checkout process reduces customer friction, leading to higher conversion rates and lower cart abandonment rates. Offering multiple payment methods and mobile optimization ensures customers can complete their purchases quickly, regardless of their preferred payment method or device.
Global Reach
Payment gateways with multi-currency support and multiple payment method options enable businesses to cater to an international audience. This expands your market reach and allows you to attract and retain customers worldwide.
Benefits of Payment Processors
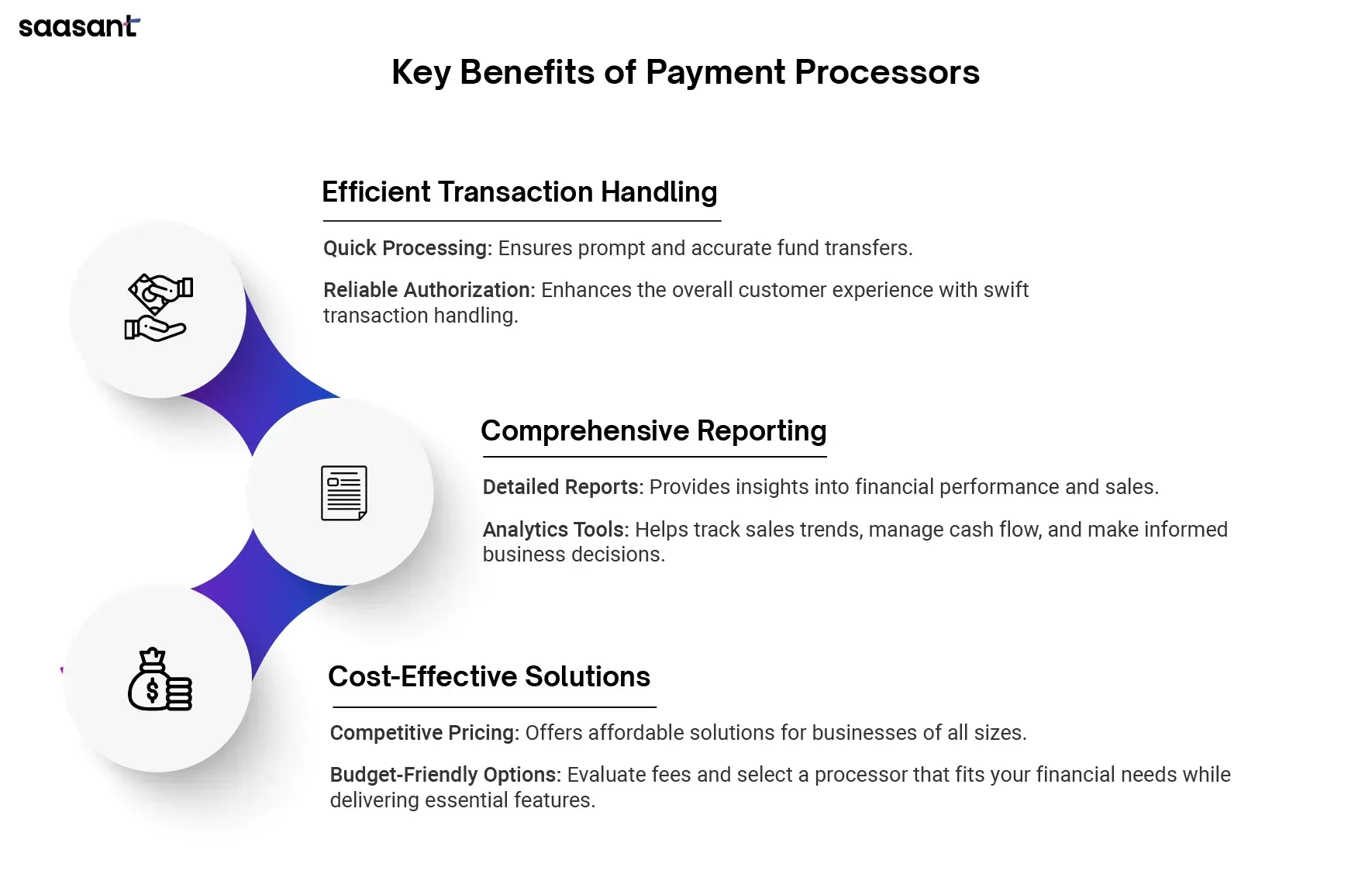
Efficient Transaction Handling
Payment processors ensure that transactions are handled efficiently, from authorization to settlement. Quick and reliable processing times enhance the customer experience and ensure that funds are transferred promptly and accurately.
Comprehensive Reporting
Detailed transaction reports and sales analytics provide businesses valuable insights into their financial performance. These tools help you track sales, manage cash flow, and identify trends that can inform business strategies and improve decision-making.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Payment processors often offer competitive pricing structures that make them a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. By carefully evaluating the fees and costs associated with different payment processors, you can choose an option that fits your budget while providing the features and benefits your business needs.
Considering Costs and Fees of Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Understanding the costs and fees associated with payment gateways and payment processors is essential for selecting the most cost-effective solution for your business. These costs can significantly impact your bottom line, so analyzing them in detail is critical.
Costs and Fees of Payment Gateways
Transaction Fees
Percentage-Based Fees: Payment gateways typically charge a percentage of each transaction amount, ranging from 2% to 3%. This fee structure is typical for credit and debit card transactions.
Flat Fees: Some payment gateways may charge a flat fee per transaction, usually in addition to the percentage-based fee. This can benefit businesses with high-value transactions, providing more predictable costs.
Setup and Monthly Fees
Setup Fees: Some payment gateways charge a one-time setup fee for integrating their service with your website or application. This fee covers configuring the gateway and ensuring it works seamlessly with your existing systems.
Monthly Fees: Recurring monthly fees may apply, which cover the cost of maintaining the payment gateway service. These fees can vary based on the features and services included in your plan.
Additional Fees
Chargeback Fees: Fees incurred when a customer disputes a transaction and initiates a chargeback, typically ranging from $15 to $25 per chargeback. Understanding these fees is crucial for managing potential disputes and minimizing financial losses.
Refund Fees: Processing refund fees may be a flat fee or a percentage of the refunded amount. These fees can add up if your business processes a high volume of refunds.
Currency Conversion Fees: Businesses with international customers must pay fees to convert transactions to different currencies. These fees can impact profitability, so it's essential to understand the conversion rates and associated costs.
Costs and Fees of Payment Processors
Transaction Fees
Percentage-Based Fees: Payment processors charge a percentage of each transaction, similar to payment gateways. These fees typically cover the cost of authorizing and settling transactions.
Interchange Fees: Fees paid to the card-issuing bank and card network, typically included in the overall transaction fee. Interchange fees can vary based on the type of card and transaction volume.
Monthly and Annual Fees
Monthly Fees: Some payment processors charge a monthly fee for using their service, covering account maintenance and customer support. These fees can vary based on the level of service and features included in your plan.
Annual Fees: Annual fees may apply, particularly for higher-tier service plans with additional features. These fees cover the cost of maintaining your account and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Additional Fees
Chargeback Fees: Like payment gateways, processors charge fees for handling chargebacks. These fees cover the cost of investigating and resolving disputes.
PCI Compliance Fees: These fees may be charged annually to ensure compliance with PCI-DSS standards. They cover the cost of maintaining secure payment practices and protecting customer data.
Batch Fees: Fees for processing daily transactions, typically a small fixed amount per batch. These fees cover settling multiple transactions at once and ensuring accurate fund transfers.
Analyzing Costs and Benefits
Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership by adding up all relevant fees, including transaction fees, setup fees, monthly fees, and additional fees. Compare this against your budget and transaction volume to determine affordability.
Value for Money
Assess the value the payment solution provides in terms of features, security, and user experience. A slightly higher cost may be justified if the solution offers significant benefits that enhance your business operations and customer satisfaction.
Break-Even Analysis
Perform a break-even analysis to determine at what transaction volume the payment solution becomes cost-effective. This helps in understanding the long-term financial impact and planning for future growth.
Best Practices for Using Payment Gateways and Processors: Tips and Best Practices for Maximizing Efficiency
Choosing the right payment gateway and processor is essential for ensuring efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. This section outlines best practices for optimizing payment gateways and processors to enhance business operations and improve customer experience.
Select the Right Payment Gateway for Your Business Needs
Choosing the appropriate payment gateway involves considering various factors, including transaction fees, security features, and integration capabilities. Evaluate the following:
Transaction Fees: Compare fees across different gateways to find the most cost-effective option. Some gateways charge a flat fee per transaction, while others take a percentage of the transaction amount. Understanding these fees can help you manage your budget effectively.
Security Features: Ensure the gateway complies with PCI DSS standards and offers robust fraud detection tools. Look for features like end-to-end encryption, tokenization, and 3D Secure authentication to safeguard customer data.
Integration: Check compatibility with your e-commerce platform and ease of integration. A payment gateway that integrates seamlessly with your existing systems can save time and reduce potential technical issues. Additionally, consider gateways that offer plugins or APIs for customization.
Ensure PCI Compliance
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance protects sensitive customer information. Follow these guidelines:
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to ensure ongoing compliance. This includes reviewing your security policies, procedures, and technologies to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Data Encryption: Store and transmit cardholder data using robust encryption methods. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, unauthorized parties cannot read or use it.
Access Control: Implement strict access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure employees have access only to the information necessary for their role.
Optimize Checkout Experience
A smooth and efficient checkout process can significantly reduce cart abandonment rates. Consider the following practices:
Simplify the Process: Minimize the number of steps required to complete a purchase. Remove unnecessary fields and steps that could frustrate or confuse customers.
Mobile Optimization: Ensure your checkout process is mobile-friendly, as many transactions occur on mobile devices. This includes responsive design, easy-to-click buttons, and mobile wallet integration.
Multiple Payment Options: Offer various payment methods to cater to diverse customer preferences. This includes credit/debit cards, digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, and alternative payment methods like PayPal, Afterpay, and cryptocurrency.
Monitor and Analyze Transactions
Regular monitoring and analysis of transactions can help identify potential issues and areas for improvement. Implement these strategies:
Transaction Reports: Generate detailed transaction reports to track payment trends and identify anomalies. Look for patterns that could indicate fraud or inefficiencies.
Customer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback to address any payment-related concerns. This can be done through surveys, reviews, or direct customer service interactions. Businesses can also trigger instant feedback collection right after a successful payment by displaying a QR code linked to a short survey—easily created using tools like Uniqode’s QR code Generator.
Fraud Detection: Utilize advanced fraud detection tools to monitor for suspicious activities. These tools can use machine learning and behavioral analytics to identify potentially fraudulent transactions.
Enhance Security Measures
Strengthening security measures is vital for building trust and protecting your business from cyber threats. Adopt these best practices:
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement 2FA for an additional layer of security during transactions. This requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing an account or completing a transaction.
Tokenization: Use tokenization to replace sensitive card information with unique tokens. This ensures that even if data is breached, it cannot be used for fraudulent transactions.
Regular Updates: Keep your payment systems and software updated to protect against the latest security vulnerabilities. This includes applying patches, updates, and new security features as they become available.
Leverage Data Insights
Utilizing data insights from your payment gateway can provide valuable information for improving business operations. Consider these approaches:
Sales Analytics: Analyze sales data to understand customer behavior and preferences. This can help you tailor marketing strategies, optimize product offerings, and improve customer service.
Performance Metrics: Monitor key performance metrics to gauge the efficiency of your payment gateway. These include transaction success rates, average transaction values, and customer satisfaction scores.
A/B Testing: Conduct A/B testing to optimize different elements of your checkout process. This can help you identify the most effective design, messaging, and functionality for improving conversion rates.
Ensure Seamless Integration with Accounting Software
Integrating your payment gateway with accounting software like QuickBooks can streamline financial management. Benefits include:
Automated Reconciliation: Automatically reconcile transactions to reduce manual errors. This saves time and ensures accuracy in your financial records.
Real-Time Reporting: Access real-time financial reports for better decision-making. This allows you to track performance, manage cash flow, and plan for the future.
Enhanced Accuracy: Minimize manual data entry to ensure accurate financial records, reducing the risk of errors and discrepancies in your accounting.
Implementing these best practices for using payment gateways and processors can significantly enhance your business's efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. By selecting the right payment gateway, ensuring PCI compliance, optimizing the checkout experience, monitoring transactions, enhancing security, leveraging data insights, and integrating with accounting software, you can create a seamless and secure payment process that benefits your business and your customers.
For those using QuickBooks, consider integrating SaasAnt Transactions to streamline your financial processes and ensure accurate and efficient transaction management. By adopting these practices, your business can stay ahead in the competitive e-commerce landscape, providing a superior payment experience for your customers.
Common Challenges and Solutions While Using Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Technical issues with payment gateways and processors can disrupt business operations and negatively impact customer experience. Addressing these challenges promptly and efficiently is crucial for maintaining smooth transactions and customer satisfaction. Below are some common technical issues and their resolutions.
Integration Problems
Issue
Integrating a payment gateway with your e-commerce platform can sometimes lead to compatibility issues, causing errors or failed transactions.
Solution
Consult Documentation: Review the payment gateway's integration documentation thoroughly and ensure your platform meets all requirements.
Use Plugins or APIs: To simplify the integration process, utilize the plugins or APIs provided by the payment gateway.
Seek Expert Assistance: If integration issues persist, consider hiring a developer with experience in payment gateway integrations.
Payment Failures
Issue
Payment failures can occur for various reasons, such as connectivity issues, incorrect payment details, or gateway errors.
Solution
Connectivity Checks: Ensure a stable internet connection and check for network-related issues.
Error Logs: Review error logs to identify the cause of the payment failure. Common issues include incorrect card details or insufficient funds.
Gateway Support: Contact the payment gateway's support team for assistance if the issue is on their end.
Slow Transaction Processing
Issue
Slow transaction processing can frustrate customers and lead to cart abandonment.
Solution
Optimize Code: Ensure your website's code is optimized for performance, reducing loading times and improving overall speed.
Server Capacity: If necessary, check your server capacity and upgrade to handle higher transaction volumes.
Payment Gateway Settings: Review and adjust the payment gateway settings to streamline the processing time.
Multi-Currency Handling
Issue
Handling multiple currencies can be complex and may lead to errors in conversion rates or transaction processing.
Solution
Enable Multi-Currency Support: Choose a payment gateway that supports multiple currencies and enables automatic conversion.
Regular Updates: Keep exchange rates updated regularly to ensure accurate conversions.
Customer Communication: Inform customers of applicable currency conversion fees or exchange rates.
Security Concerns While Using Payment Gateways & Payment Processors
Addressing Security Concerns While Using Payment Gateways & Payment Processors and Ensuring Compliance.
Security is paramount in online transactions, as breaches can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Ensuring compliance with security standards and implementing robust security measures can mitigate these risks. Here are some common security concerns and their solutions.
Data Breaches
Issue: Data breaches can compromise sensitive customer information, leading to financial loss and loss of trust.
Solution:
PCI DSS Compliance: Ensure your payment gateway complies with PCI DSS standards, which provide guidelines for securely handling cardholder data.
Encryption: Use robust encryption methods to protect data during transmission and storage.
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Fraudulent Transactions
Issue: Fraudulent transactions can result in chargebacks and financial losses for your business.
Solution:
Fraud Detection Tools: Implement advanced fraud detection tools that use machine learning and behavioral analytics to identify suspicious transactions.
3D Secure Authentication: Enable 3D Secure authentication for an additional layer of security, requiring customers to verify their identity during the transaction process.
Transaction Monitoring: Monitor real-time transactions and flag any unusual or high-risk activities for further review.
Phishing Attacks
Issue: Phishing attacks can trick customers into providing sensitive information, leading to unauthorized transactions.
Solution:
Customer Education: Educate customers about phishing attacks and how to recognize suspicious emails or messages.
Secure Communication Channels: Ensure all customer communication is conducted through secure, verified channels.
Email Authentication: Implement protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent email spoofing.
Compliance with Global Regulations
Issue: International businesses can be challenging to navigate and comply with global regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Solution:
Legal Consultation: Consult legal experts to understand and comply with relevant data protection and privacy regulations.
Data Protection Policies: Implement robust data protection policies and practices, including obtaining customer consent for data processing.
Regular Updates: Stay informed about regulation changes and update your policies and practices accordingly.
Addressing technical issues and security concerns is essential for maintaining a smooth and secure payment process in e-commerce. Proactively managing integration problems, payment failures, slow transaction processing, and multi-currency handling can ensure efficient operations. Simultaneously, prioritizing security measures such as PCI DSS compliance, encryption, fraud detection, and phishing prevention will protect your business and customers from potential threats.
Ensuring compliance with global regulations and keeping abreast of evolving security practices will further enhance your payment processing capabilities. By implementing these solutions, your business can provide a secure and reliable payment experience, fostering customer trust and satisfaction in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Wrap Up
Selecting the right payment solution for your business is a critical decision that can significantly impact your operations, customer satisfaction, and overall success. Understanding the differences between payment gateways and payment processors is essential to making an informed choice.
A payment gateway is an intermediary that securely captures and transfers payment information from customers to the acquiring bank. It offers a seamless and secure checkout experience, which is essential for building trust and enhancing customer satisfaction. On the other hand, a payment processor handles the transaction's backend, ensuring that funds are transferred from the customer's account to the merchant's account efficiently and reliably.
When choosing the right solution, consider your business's specific needs. A comprehensive payment gateway may be optimal if you require robust security features, seamless integration with your e-commerce platform, and a smooth customer experience. Conversely, focusing on a reliable payment processor might be more beneficial if your primary concern is efficiently handling transaction processing with competitive fees.
Additionally, consider the solution's scalability. As your business grows, your payment needs will evolve. Opt for a solution that accommodates increased transaction volumes and offers advanced features, such as multi-currency support and fraud detection.
Integrating a payment gateway and a payment processor that work harmoniously can provide a comprehensive solution, ensuring optimization of both the front-end user experience and back-end transaction management. Leveraging advanced technologies and staying updated with industry trends will keep your business competitive and responsive to customer expectations.
To further streamline your financial operations, consider utilizing applications like SaasAnt Transactions, which can seamlessly integrate with your accounting software, such as QuickBooks. This integration ensures accurate financial records and simplifies the reconciliation of payment transactions, enhancing overall efficiency.
The right payment solution blends security, efficiency, and scalability. Carefully evaluate your business requirements and choose a solution that meets your current needs and supports your future growth. By making an informed decision and leveraging comprehensive applications like SaasAnt Transactions, you can enhance your payment processes, foster customer trust, and drive your business toward sustained success.
FAQs
What Is the Main Difference Between a Payment Gateway and a Payment Processor?
The primary difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor lies in their functions within the payment ecosystem. A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates the secure transmission of payment information from a customer's device to the merchant's bank. It acts as a digital bridge, ensuring that transaction data is encrypted and sent securely to the payment processor.
In contrast, a payment processor handles the transaction data once it is received from the gateway. It manages the authorization and settlement of payments, ensuring that funds are transferred from the customer's bank account to the merchant's account. Essentially, while the payment gateway captures and transmits payment information, the payment processor executes the financial transaction.
Can I Use Both a Payment Gateway and a Payment Processor?
Yes, you can use both a payment gateway and a payment processor in tandem, and it is often the recommended approach for businesses seeking a comprehensive payment solution. Many payment service providers offer integrated solutions that include both functionalities. The payment gateway captures and encrypts customer payment data, while the payment processor handles the authorization and transfer of funds. Utilizing both services together ensures a secure and efficient transaction process, enhancing merchants' and customers' overall payment experience.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Payment Gateway?
Using a payment gateway offers several significant benefits:
Security: Payment gateways encrypt sensitive payment information, protecting it from fraud and data breaches. This ensures that customer data is handled securely throughout the transaction process.
Seamless Integration: Payment gateways integrate seamlessly with e-commerce platforms, providing a smooth checkout experience for customers and minimizing cart abandonment.
Global Reach: Many payment gateways support multiple currencies and payment methods, allowing businesses to cater to a worldwide audience and expand their market reach.
Enhanced User Experience: Payment gateways offer user-friendly interfaces and streamlined checkout processes, which contribute to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
Fraud Prevention Tools: Advanced fraud detection and prevention tools are often included, helping businesses identify and mitigate fraudulent transactions.
Is Amazon Pay a Payment Gateway or Processor?
Amazon Pay functions primarily as a payment gateway. It enables merchants to offer Amazon's payment experience to their customers, allowing them to use their Amazon account for transactions. Amazon Pay facilitates the secure transmission of payment information and integrates with existing payment processors to handle the actual transaction processing. By leveraging Amazon Pay, merchants benefit from Amazon’s established security measures and customer trust while simplifying the checkout process for users.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Payment Processor?
Using a payment processor provides several key benefits:
Efficient Transaction Management: Payment processors handle the authorization, settlement, and transfer of funds, ensuring that transactions are processed quickly and accurately.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Payment processors often offer competitive pricing structures, including transaction fees and service charges, which can be beneficial for managing operational costs.
Scalability: Payment processors support varying transaction volumes and can scale with your business as it grows, accommodating increased processing needs without compromising performance.
Integration with Financial Systems: Payment processors integrate with accounting and financial systems, simplifying payment reconciliation and improving overall financial management.
Access to Reporting Tools: Many payment processors provide detailed reporting and analytics tools, enabling businesses to monitor transaction trends, track performance, and make data-driven decisions.
How Do I Choose Between a Payment Gateway and a Payment Processor?
Choosing between a payment gateway and a payment processor depends on your business needs and the specific features required:
Functionality: Determine whether you need a solution primarily to capture and secure payment information (payment gateway) or manage the authorization and transfer of funds (payment processor). Many businesses opt for integrated solutions that offer both functionalities.
Business Size and Volume: Consider your transaction volume and business size. Larger businesses or those with high transaction volumes might benefit from a dedicated payment processor, while smaller companies may find integrated solutions more cost-effective.
Security Requirements: Evaluate your security needs. Payment gateways offer robust security features but ensure your payment processor adheres to industry fraud prevention and data protection standards.
Integration Needs: Assess how well the payment solution integrates with your existing e-commerce platform and financial systems. Seamless integration can enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
Cost Considerations: Compare the fees associated with different payment gateways and processors. Look for a solution that aligns with your budget while meeting your operational and security requirements.