Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Importance & Calculation
 The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a critical financial metric that businesses use to evaluate how efficiently they collect customer debts. This guide delves into the nuances of this ratio, highlighting its significance and offering practical advice for calculating and improving it.
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a critical financial metric that businesses use to evaluate how efficiently they collect customer debts. This guide delves into the nuances of this ratio, highlighting its significance and offering practical advice for calculating and improving it.
Contents
What is the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
Importance of the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
How to Calculate Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
Interpreting the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Improving Your Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Common Challenges and Solutions
Conclusion
FAQs
What is the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how often a company collects its average accounts receivable during a specific period. This ratio provides insights into the effectiveness of a company's credit policies and collection processes.
Importance of the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Understanding the accounts receivable turnover ratio is crucial for businesses because it significantly impacts cash flow and overall financial health. This ratio measures how effectively a company collects its outstanding credit sales and manages its accounts receivable. By examining this metric, businesses can gain insights into their credit policies and collection efficiency.
A higher accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that a company efficiently collects its receivables. This efficiency can lead to several positive outcomes:
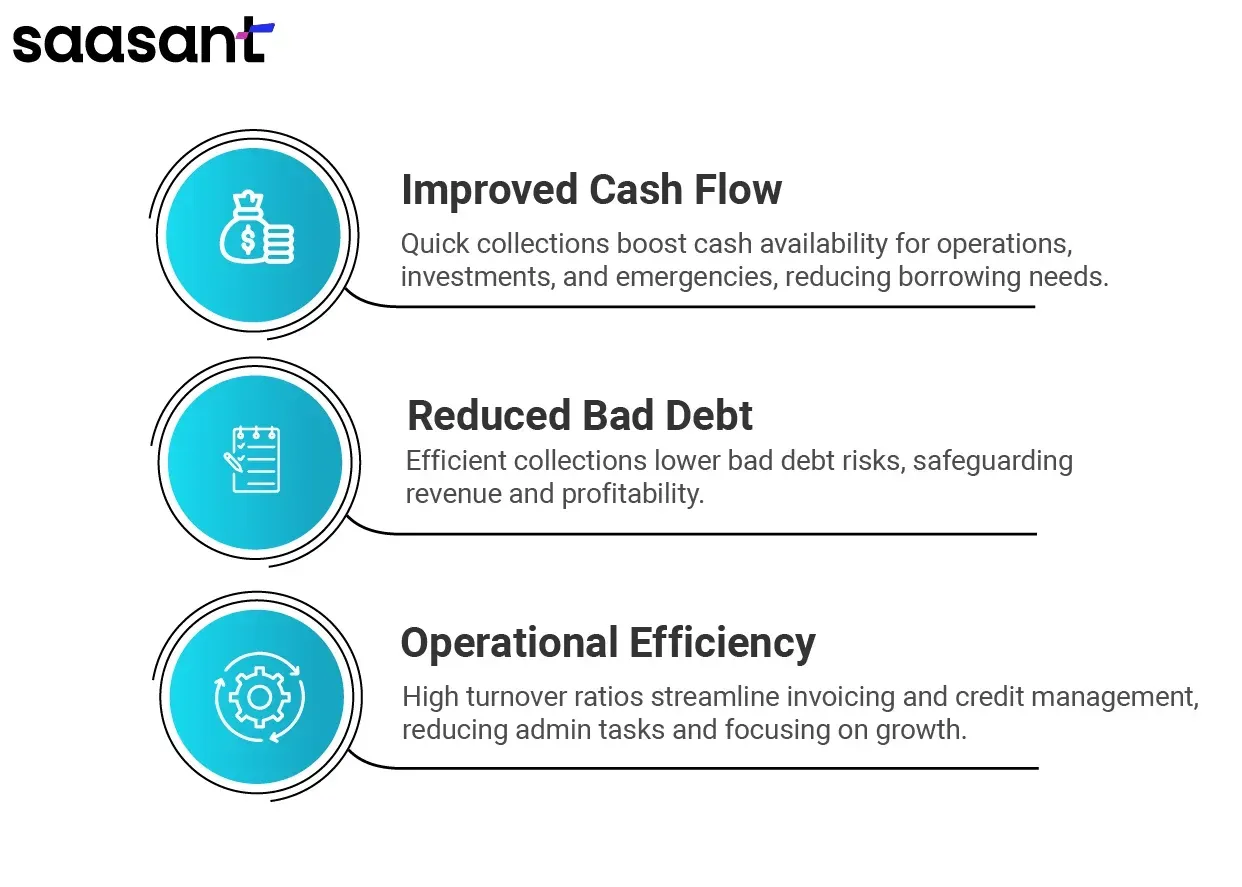
Improved Cash Flow: Quick collection of receivables means more cash is available for daily operations, investments, and unexpected expenses. This enhanced cash flow helps maintain liquidity and reduces the need for borrowing.
Reduced Bad Debt: Efficient collection processes minimize the risk of bad debt. Companies with high turnover ratios are less likely to face issues with customers defaulting on payments, which protects their revenue and profitability.
Operational Efficiency: A high turnover ratio often reflects streamlined invoicing and effective credit management. Businesses can reduce administrative burdens and focus on growth and strategic initiatives by minimizing the time and resources spent chasing late payments.
Conversely, a lower accounts receivable turnover ratio can signal potential problems:
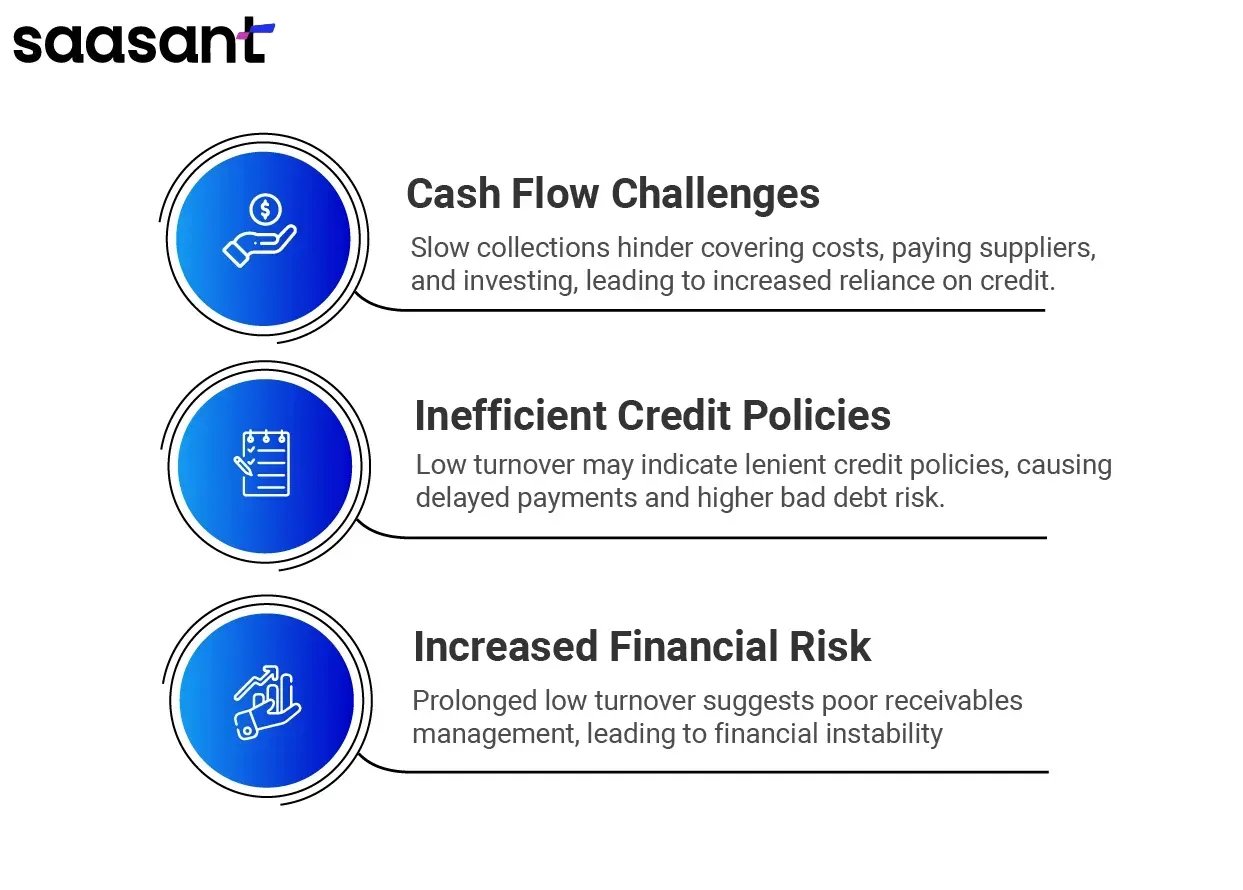
Cash Flow Challenges: Slow collection of receivables can lead to cash flow problems, making it difficult to cover operational costs, pay suppliers, or invest in growth opportunities. This situation can force businesses to rely on credit or loans, increasing financial risk.
Inefficient Credit Policies: A low turnover ratio may indicate that the company’s credit policies are too lenient, allowing customers to take longer to pay. This leniency can result in delayed payments and increased exposure to bad debt.
Increased Financial Risk: Prolonged periods of low turnover can indicate deeper financial issues within the company. They may suggest that the business needs to manage its receivables more effectively can lead to financial instability and affect overall business performance.
How to Calculate Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Formula
The formula for calculating the accounts receivable turnover ratio is:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales/Average Accounts Receivable.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Determine Net Credit Sales: Sum up all sales made on credit over a specific period.
Calculate Average Accounts Receivable: Add the period's beginning and ending accounts receivable balances, then divide by two.
Apply the Formula: Divide net credit sales by the average accounts receivable.
Example Calculation
For example, if a company has net credit sales of $500,000 and an average accounts receivable of $100,000, the accounts receivable turnover ratio would be:
Ratio=500,000/100,000=5
This means the company collects its average receivables five times a year.
Interpreting the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
High vs. Low Turnover Ratios
A high turnover ratio typically indicates efficient collection processes and good credit policies. Conversely, a low turnover ratio may suggest inefficiencies and potential issues with receivable collections.
Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
To gauge the effectiveness of your ratio, compare it against industry benchmarks. This comparison helps identify areas for improvement and sets realistic targets.
Improving Your Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Best Practices for Accounts Receivable Management
Implementing best practices can significantly enhance the accounts receivable turnover ratio. These include regular review of credit policies, effective customer communication, and streamlined invoicing processes.
Enhancing Credit Policies
Improving credit policies is a multifaceted approach involving several vital practices to ensure timely payments and reduce credit risk. Here are some critical steps:

Setting Clear Credit Terms: Define clear credit terms that specify payment deadlines, penalties for late payments, and any early payment discounts. This transparency helps customers understand their obligations and encourages timely payments.
Conducting Thorough Credit Checks: Before extending credit to new customers, perform comprehensive credit checks to assess their creditworthiness. This includes reviewing credit scores, financial statements, and payment histories with other suppliers.
Regularly Reviewing Credit Limits: Monitor and adjust credit limits based on customers’ payment behaviors and financial stability. Customers with a history of late payments may need lower credit limits, while reliable payers might warrant higher limits.
Implementing Credit Policies: Communicate credit policies to all relevant staff and ensure consistent enforcement. Regular training and updates can help maintain adherence to these policies.
Utilizing Credit Insurance: Consider credit insurance to protect against potential losses from non-paying customers. This can provide an added layer of security for your receivables.
Establishing a Credit Committee: Form a committee responsible for reviewing and approving significant credit decisions. This ensures a balanced approach and mitigates risks associated with extending credit.
Efficient Invoicing and Collections
Timely invoicing and proactive collections are crucial components of effective accounts receivable management. Here’s how to enhance these processes:

Automated Invoicing Systems: Utilize automated invoicing systems to ensure invoices are generated and sent promptly. Automation reduces the risk of human error and ensures consistency in billing cycles.
Clear and Detailed Invoices: Ensure that invoices are clear, detailed, and easy to understand. Include all necessary information, such as payment terms, due dates, and payment methods, to avoid confusion and delays.
Regular Follow-Up: Implement a systematic approach for following up on overdue accounts. Use reminders and follow-up emails to prompt customers about upcoming and past-due payments.
Proactive Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with customers. Address any disputes or issues promptly to prevent payment delays. Establishing good relationships can facilitate smoother payment processes.
Incentives for Early Payments: Offer discounts or other incentives for early payments to encourage customers to pay their invoices before the due date.
Flexible Payment Options: Provide multiple payment options, such as credit cards, online payments, and bank transfers, to help customers settle their invoices promptly.
Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitor accounts receivable aging reports to identify and address overdue accounts. This helps in prioritizing collection efforts and improving cash flow.
Collection Policies and Procedures: Establish clear procedures for handling late payments, including escalation processes and potential legal actions if necessary. Ensure that these policies are consistently applied.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with Slow-Paying Customers
Addressing slow payments requires a strategic approach to ensure that cash flow remains steady and customer relationships are maintained. Here are several tactics to manage slow-paying customers effectively:
Early Payment Discounts: Offer incentives such as discounts for early payments. For example, a 2% discount if payment is made within ten days can motivate customers to pay sooner rather than later.
Setting Up Payment Plans: For customers struggling to pay their invoices in full, consider setting up structured payment plans. This can help them manage their cash flow while ensuring you receive payments regularly.
Regular Communication: Maintain open and frequent communication with customers. Regular follow-ups through phone calls, emails, or reminder letters help customers remember their payment obligations.
Clear Invoicing: Ensure that invoices are clear, accurate, and sent promptly. Any errors or delays can give customers an excuse to postpone payment.
Personalized Approaches: Tailor your communication based on the customer’s payment history and relationship with your business. Personalized approaches can be more effective in eliciting timely payments.
Automated Reminders: Use automated systems to send payment reminders as due dates approach. This reduces administrative workload and ensures consistent follow-up.
Late Payment Penalties: Implement and enforce late payment penalties. Clearly state these penalties in your credit terms to discourage late payments.
Building Relationships: Foster strong relationships with your customers. Understanding their financial situations and challenges can help you negotiate better terms and encourage timely payments.
Credit Holds: For consistently slow-paying customers, consider placing their accounts on credit hold until outstanding payments are settled. This measure can prompt quicker payments to continue business transactions.
Professional Collection Services: In persistent non-payment cases, professional collection agencies can help recover overdue amounts while complying with relevant laws and regulations.
Balancing Credit Risk and Sales Growth
Balancing the extension of credit to drive sales growth and managing credit risk is essential for maintaining a healthy financial position. Here are strategies to achieve this balance:
Regular Credit Assessments: Continuously assess and monitor the creditworthiness of your customers. Use credit reports, financial statements, and payment histories to make informed credit decisions.
Flexible Credit Terms: Tailor credit terms are based on each customer's risk profile. Higher-risk customers might be offered shorter payment terms or lower credit limits, while reliable customers can be granted more favorable terms.
Diversifying Customer Base: Avoid over-reliance on a few large customers for your revenue. A diverse customer base spreads the risk and ensures that one customer's non-payment does not significantly impact your cash flow.
Credit Insurance: Consider credit insurance to protect against potential losses from non-paying customers. This can provide peace of mind and financial stability.
Clear Credit Policies: Establish and communicate clear credit policies. Ensure all staff understand and adhere to these policies and that customers know the terms and conditions.
Monitoring and Adjusting Terms: Review and adjust credit terms regularly based on customer performance and changing market conditions. This proactive approach helps mitigate risk while supporting sales growth.
Using Credit Scoring Models: Implement credit scoring models to evaluate the credit risk associated with each customer objectively. This helps in making data-driven decisions about extending credit.
Setting Credit Limits: Define credit limits for each customer based on their creditworthiness and payment history. Review and adjust these limits regularly as necessary.
Incentivizing Prompt Payments: Encourage timely payments by offering incentives such as discounts for early payments or rewards for maintaining good payment records.
Continuous Training: Provide continuous training for your credit management team. Keeping them updated on best practices and industry trends helps manage credit risk effectively.
Conclusion
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a vital indicator of a company's financial health, reflecting its efficiency in collecting outstanding credit sales. Regular monitoring and proactive management of this ratio can significantly enhance cash flow, reduce the risk of bad debts, and improve financial planning. By swiftly converting receivables into cash, businesses can maintain liquidity, support operational needs, and invest in growth opportunities. A strong turnover ratio also bolsters customer relationships through clear communication and timely invoicing while providing a competitive edge by showcasing financial stability and operational efficiency. Overall, diligent oversight of this ratio leads to better business performance and stability.
FAQs
What is a good accounts receivable turnover ratio?
A good ratio varies by industry, but generally, a higher ratio indicates more efficient receivable management.
What does the accounts receivable turnover ratio measure?
It measures how often a company collects its average accounts receivable within a specific period.
What is the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Formula?
The formula is Net Credit Sales/Average Accounts Receivable
How do you interpret accounts receivable turnover?
Interpretation depends on comparing the ratio with industry standards and understanding what high or low ratios indicate about a company's receivable collection efficiency.
How often should I calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio?
Calculating this ratio quarterly or annually provides a consistent measure of receivable management efficiency.
How can I improve my accounts receivable turnover ratio?
Implement best practices for credit policies, efficient invoicing, and proactive collections to improve the ratio.
What factors can affect the accounts receivable turnover ratio?
Factors include credit policies, customer payment behaviors, and the efficiency of the invoicing and collection processes.
How does the accounts receivable turnover ratio impact cash flow?
A higher ratio improves cash flow by ensuring faster collection of receivables, while a lower ratio can lead to cash flow challenges due to delayed collections.