What is an Invoice? FAQs & Managing Invoices in QuickBooks
 In the business world, invoices are like the heartbeat of your finances. They keep things running smoothly by ensuring everyone understands what's been bought or sold, acting as legal proof of your deals, and helping you keep track of your money. This guide is your go-to source for all things invoices, from what they are to why they matter, what they should include, and how to handle them like a pro. Let’s also look at how handy accounting software like QuickBooks and Xero can make invoicing a breeze, plus some smart tips for managing invoices on online selling platforms. Whether you're a seasoned pro or just starting, this guide will help you send pro invoices, get paid on time, and keep your finances in shape.
In the business world, invoices are like the heartbeat of your finances. They keep things running smoothly by ensuring everyone understands what's been bought or sold, acting as legal proof of your deals, and helping you keep track of your money. This guide is your go-to source for all things invoices, from what they are to why they matter, what they should include, and how to handle them like a pro. Let’s also look at how handy accounting software like QuickBooks and Xero can make invoicing a breeze, plus some smart tips for managing invoices on online selling platforms. Whether you're a seasoned pro or just starting, this guide will help you send pro invoices, get paid on time, and keep your finances in shape.
Contents
What is an Invoice?
Purpose of Invoices in Business Transactions
Important Questions on Invoices
Comparing Invoices: Invoices vs. Other Documents
Automation in Invoice Management
Financial and Legal Aspects of Invoices
International Considerations for Invoicing
Security Considerations for Invoicing
Advanced Features in Invoicing Software
Conclusion
FAQs
What is an Invoice?
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer detailing the products or services provided, their prices, and the total amount due. It serves as a formal request for payment and includes essential information for both parties involved in the transaction.
Purpose of Invoices in Business Transactions
Invoices play a crucial role in business transactions by ensuring clear communication between sellers and buyers. They help track sales, manage accounts receivable, and maintain accurate financial records. Invoices also serve as legal documents, providing evidence of the agreement and terms of the sale.
Understanding Invoices: The Basics of Invoices
What is an Invoice Number?
An invoice number is a unique identifier assigned to each invoice for tracking and reference purposes. It helps both parties organize and manage their financial records.
What is an Invoice Date?
The invoice date is the date on which the invoice is issued. It marks the beginning of the payment terms and is essential for calculating the payment due date.
What is an Invoice Payment?
An invoice payment is a payment made by the buyer to the seller for the goods or services listed on the invoice. It confirms the completion of the transaction.
What is an Invoice Used For?
An invoice is used for billing purposes, requesting payment, and recording the details of a transaction. It ensures that both parties have a clear record of the sale.
What is the Purpose of an Invoice?
The primary purpose of an invoice is to document the sale of goods or services, request payment, and provide a legal record of the transaction. It also helps track sales and manage cash flow.
What is an Invoicing Example?
An example of invoice payment terms could be "Net 45," which indicates that the customer has 45 days from the invoice date to pay. An invoice due date calculator can help verify that customers adhere to these payment terms.
Invoice Components: The Details in an Invoice
Discover the essential elements of an invoice, from seller and buyer details to the total amount due. This section breaks down each component to ensure clarity and completeness in your invoicing process.
What is on an Invoice?
An invoice typically includes:
Seller’s details (name, address, contact information)
Buyer’s details (name, address, contact information)
Invoice number
Invoice date
List of items or services provided
Prices and quantities
Payment terms
Total amount due
What is an Itemized Invoice?
An itemized invoice lists each product or service provided and individual prices, quantities, and total amounts. It provides a detailed breakdown of the charges.
What is a PO Number on an Invoice?
A PO (Purchase Order) number is a reference number that links the invoice to a specific purchase order issued by the buyer. It helps in tracking and managing orders.
What is an Invoice ID?
An invoice ID is a unique identifier assigned to each invoice, similar to an invoice number. It is used for tracking and reference purposes.
What is an Invoice Address?
An invoice address is where the invoice is sent, usually the buyer’s address. For billing purposes, it can also refer to the seller's address.
What is an Invoice Price?
The invoice price is the total amount charged for the goods or services listed, including any taxes, discounts, or additional fees.
What is an Invoice in Business?
An invoice is a crucial document used to bill clients, manage accounts receivable, and keep accurate financial records. It ensures that businesses are paid for their goods and services.
Managing Invoices in QuickBooks
QuickBooks is a widely used accounting software that simplifies the invoicing process for businesses of all sizes. Here’s how to effectively manage invoices in QuickBooks:
Creating an Invoice
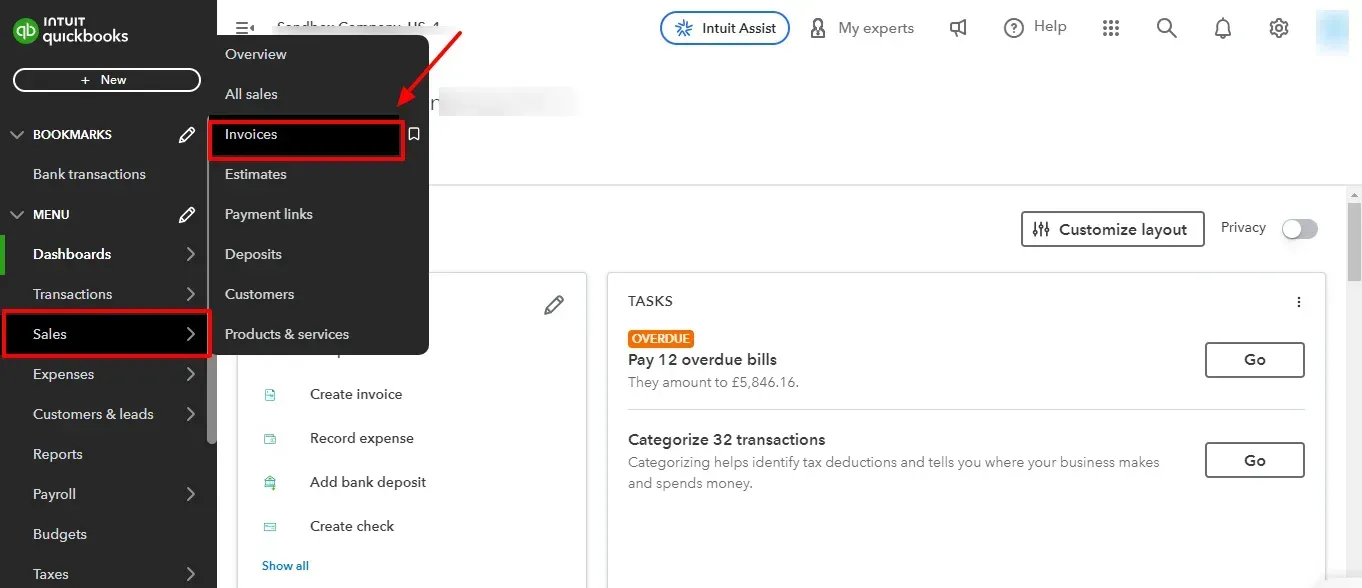
1. Navigate to Invoicing:
Open QuickBooks Online and go to the Sales tab.
Within the Sales tab, select Invoices.
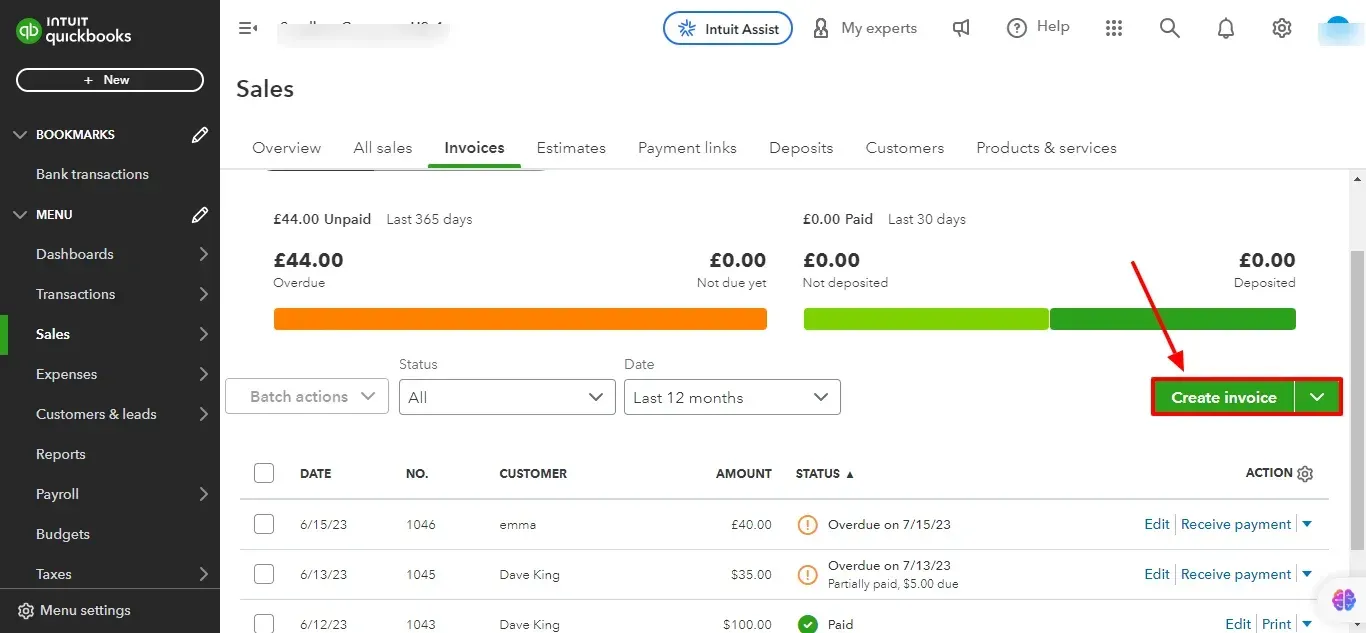
2. Create a New Invoice:
Click on the Create New Invoice button.
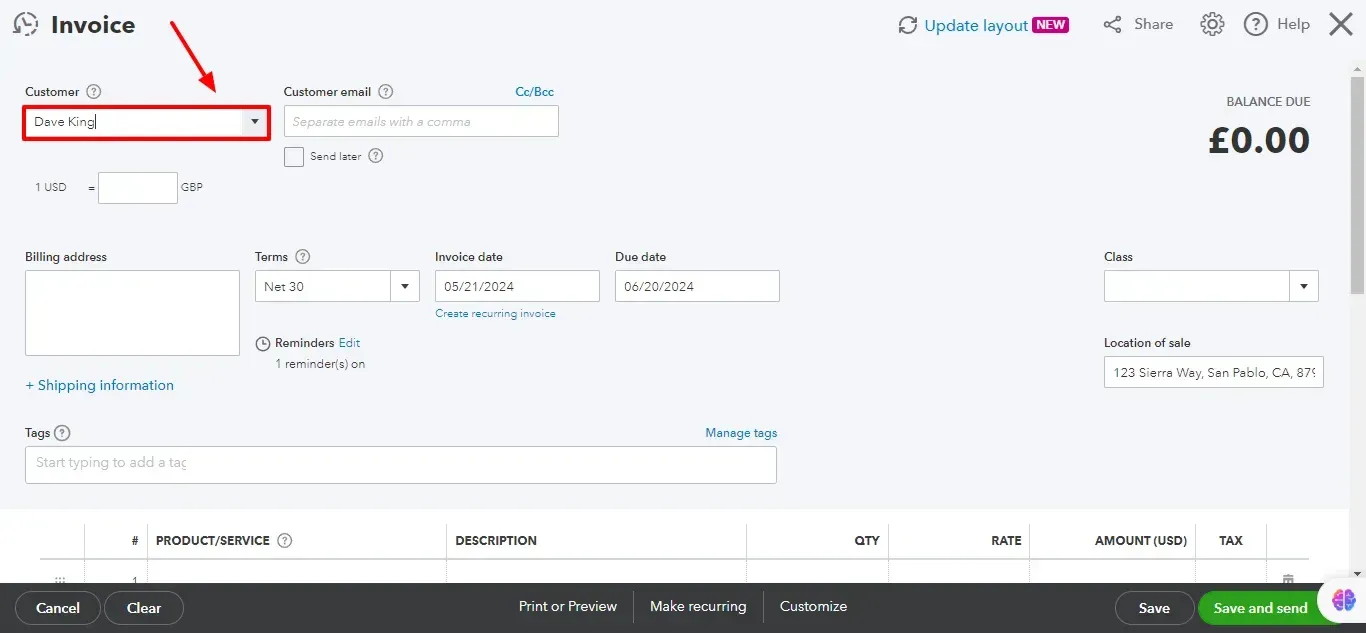
3. Fill in Customer Details:
In the Customer field, select an existing customer from the dropdown menu.
If the customer is new, click Add New and enter their details.
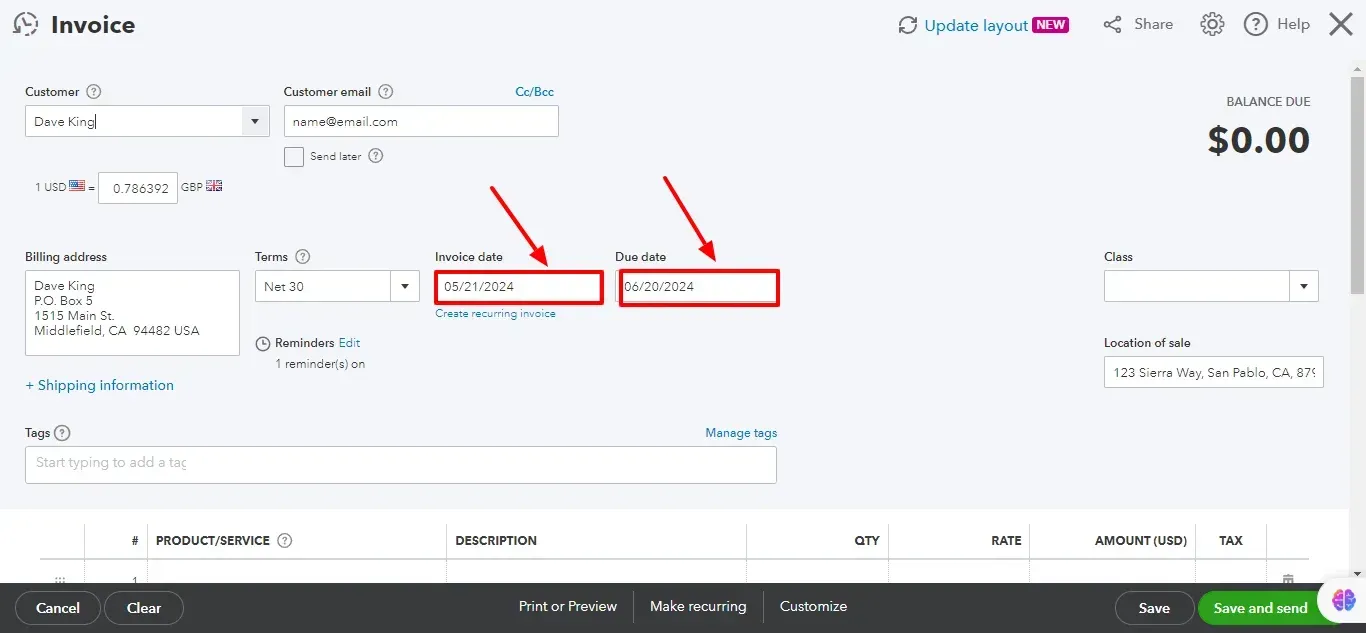
4. Set Invoice Date, Due Date, and Terms:
Enter the Invoice date (usually the date you create the invoice).
Set the Due date (the date by which you expect payment).
You can specify payment conditions in the Terms field, such as "Net 30" (payment due within 30 days).
5. Add Products or Services:
In the product or service item list, you can:
Select existing products or services from the dropdown menu.
Click + Add new to create a new product or service.
Enter the Quantity of each item sold.
Enter the Rate (price per unit) for each item.
QuickBooks will automatically calculate the Amount (quantity x rate).
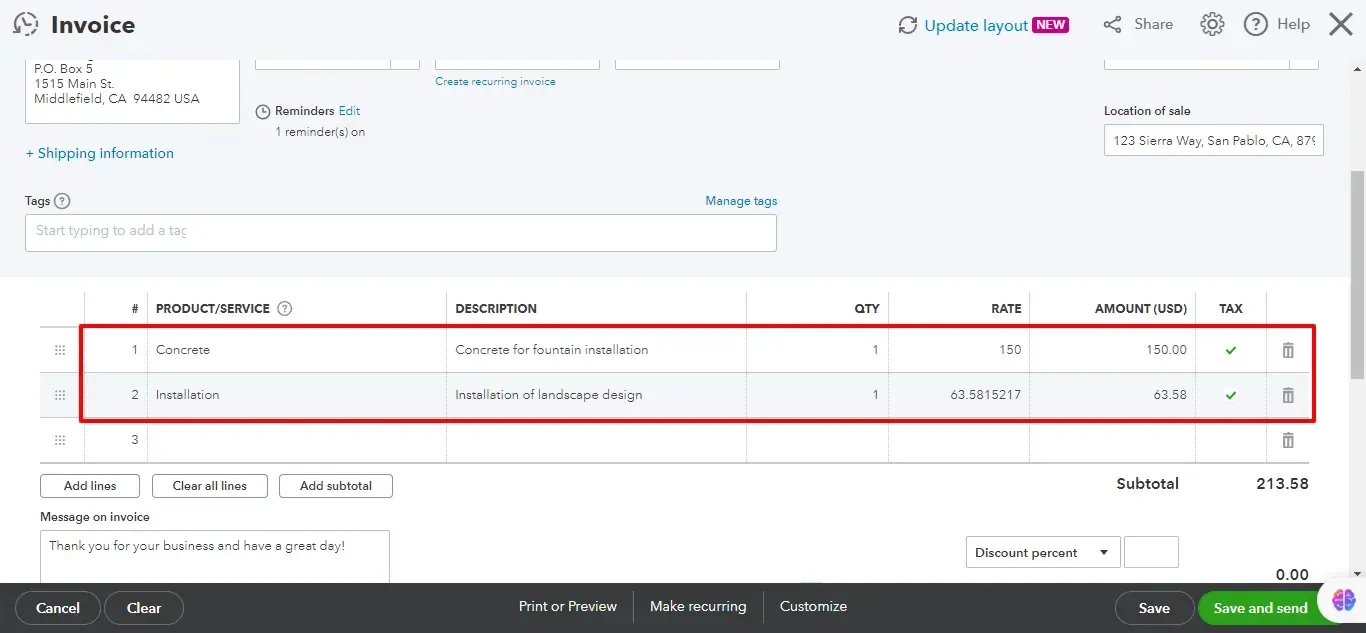
6. Customize Invoice (Optional):
Click the Gear Icon (Manage) to customize the invoice template.
You can add your company logo, adjust fonts and colors, and include a custom message for the customer.
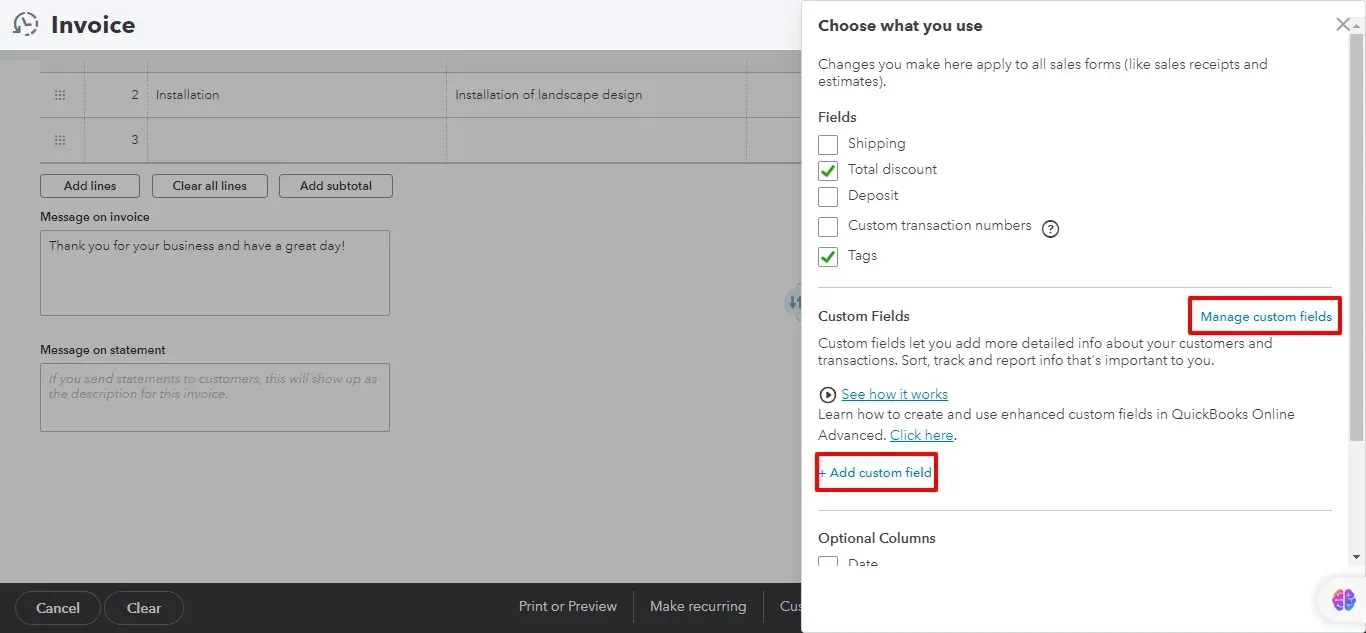
7. Save and Send Invoice:
Once you've reviewed the invoice details, click Save.
You can then Send the invoice directly to your customer's email from QuickBooks.
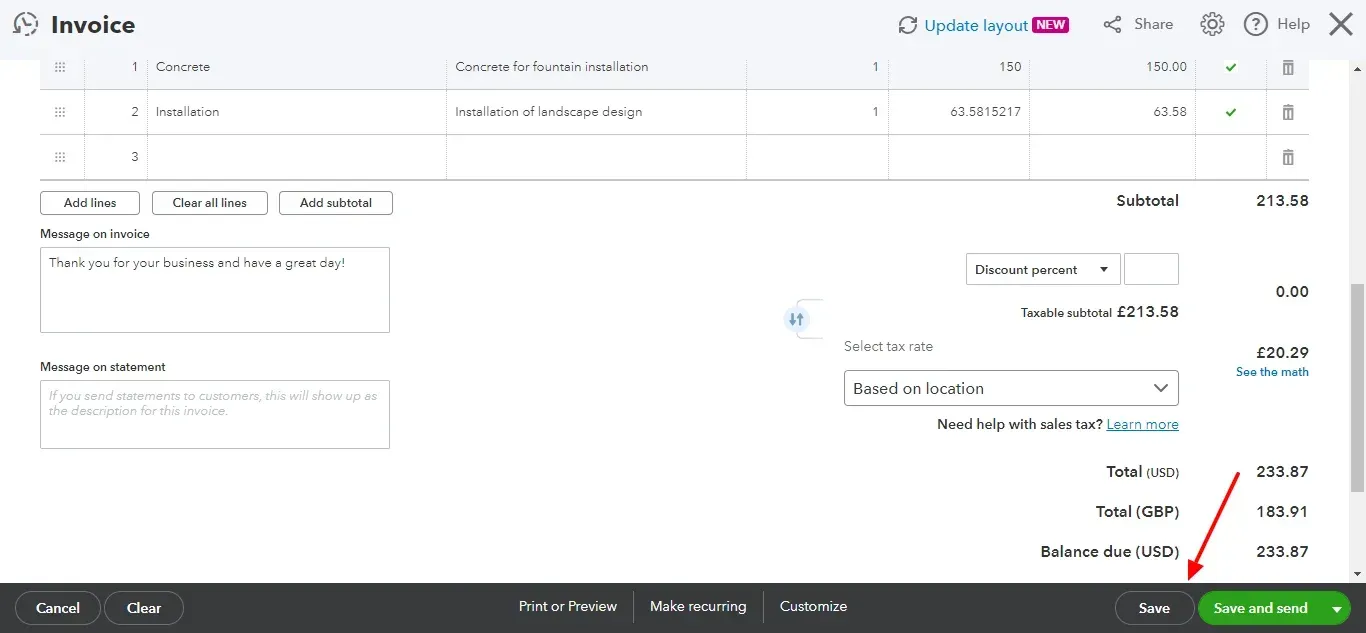
Tracking and Managing Invoices
Invoice Overview: The Invoices section contains all invoices, which can be filtered by status, such as Paid, Unpaid, or Overdue.
Payment Reminders: Set automated reminders to notify customers about due or overdue payments.
Record Payments: Log payments against invoices, updating their status to Paid. QuickBooks can also automatically match payments received via bank feeds.
Efficient Bulk Import: For businesses managing huge invoices, SaasAnt Transactions is the perfect application to import bulk invoices quickly and accurately, saving time and reducing errors. Try the SaasAnt Transactions application in the QuickBooks Appstore.
Reporting
Invoice Reports: Generate comprehensive reports on invoicing activities, such as the Sales by Customer Summary and the Invoice List report, to monitor outstanding and paid invoices.
Cash Flow Insights: Use these reports to analyze cash flow and make informed financial decisions.
Managing Invoices in Xero
Xero is renowned for its user-friendly interface and robust invoicing capabilities. Here’s how to efficiently manage invoices in Xero:
Creating an Invoice
1. Access the Sales Menu:
Open Xero and navigate to the Business tab.
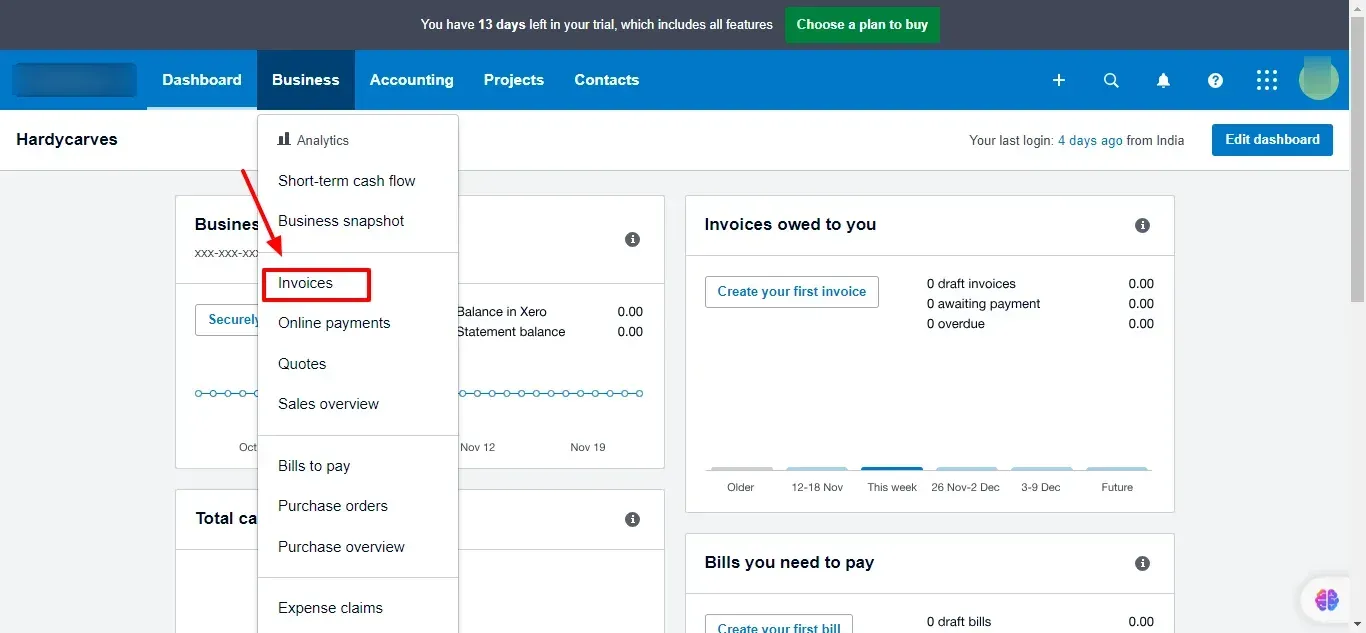
2. Create a New Invoice:
Click on Invoice -> New Invoice
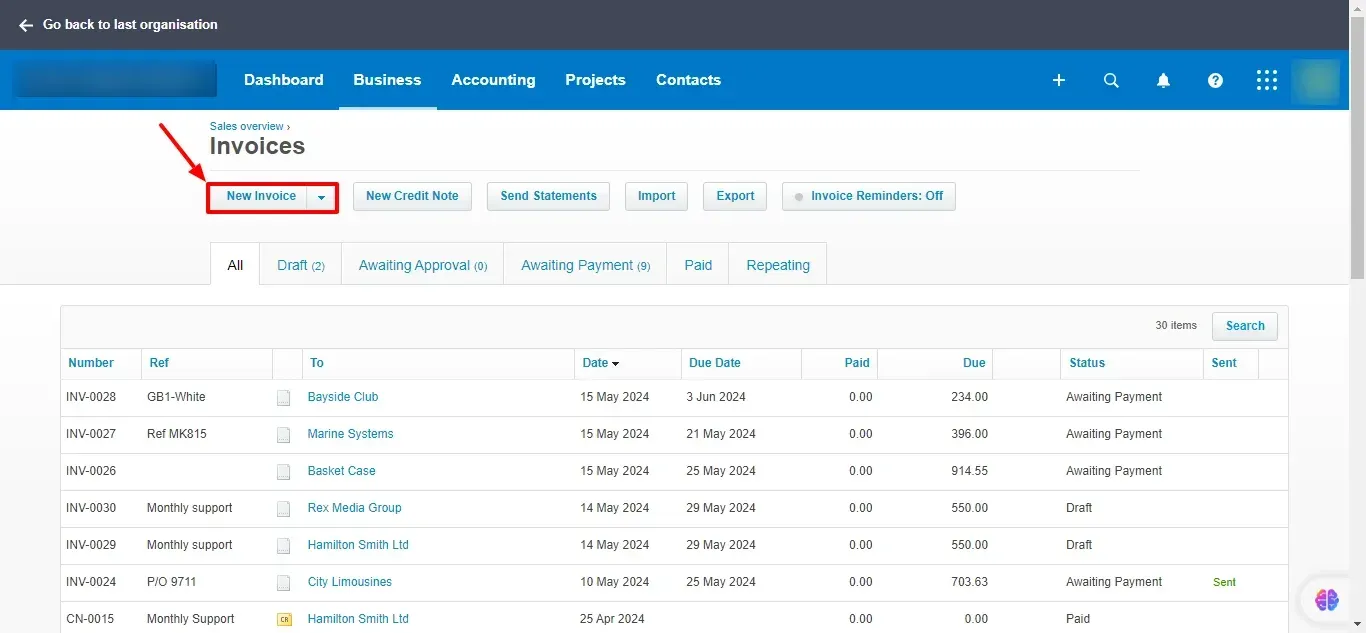
3. Enter Customer Information:
In the Customer field, select an existing customer from the dropdown list.
If the customer is new, click Add Customer and fill in their details.
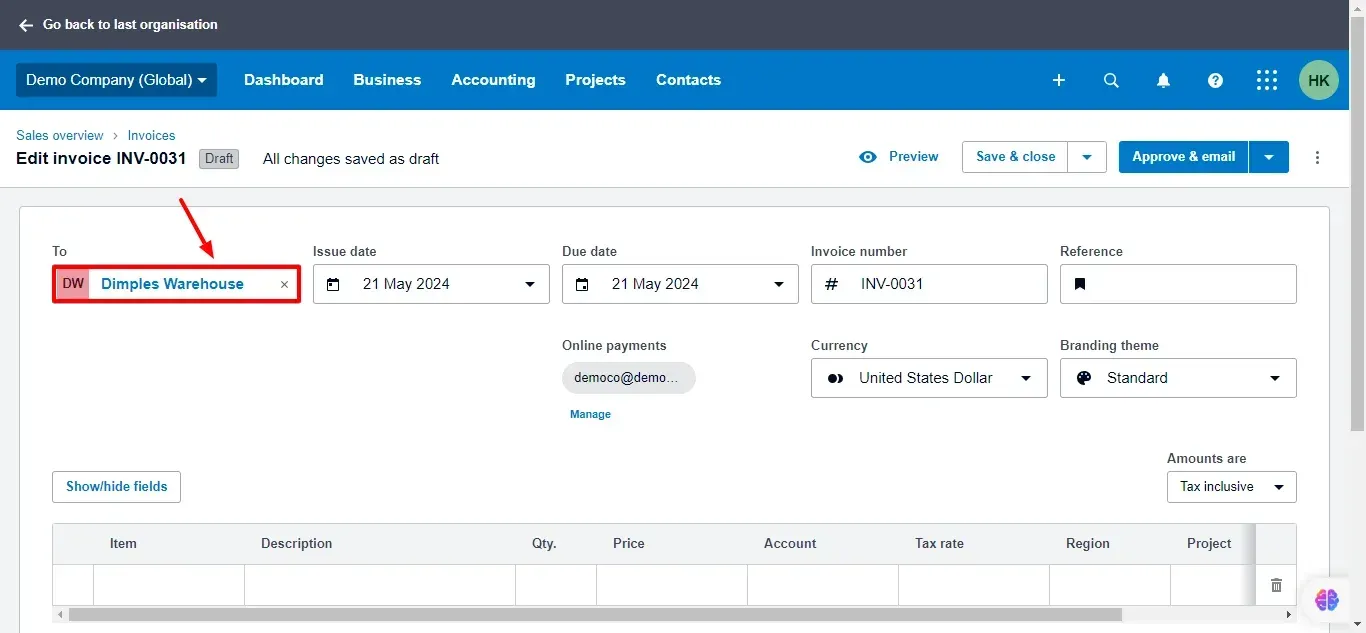
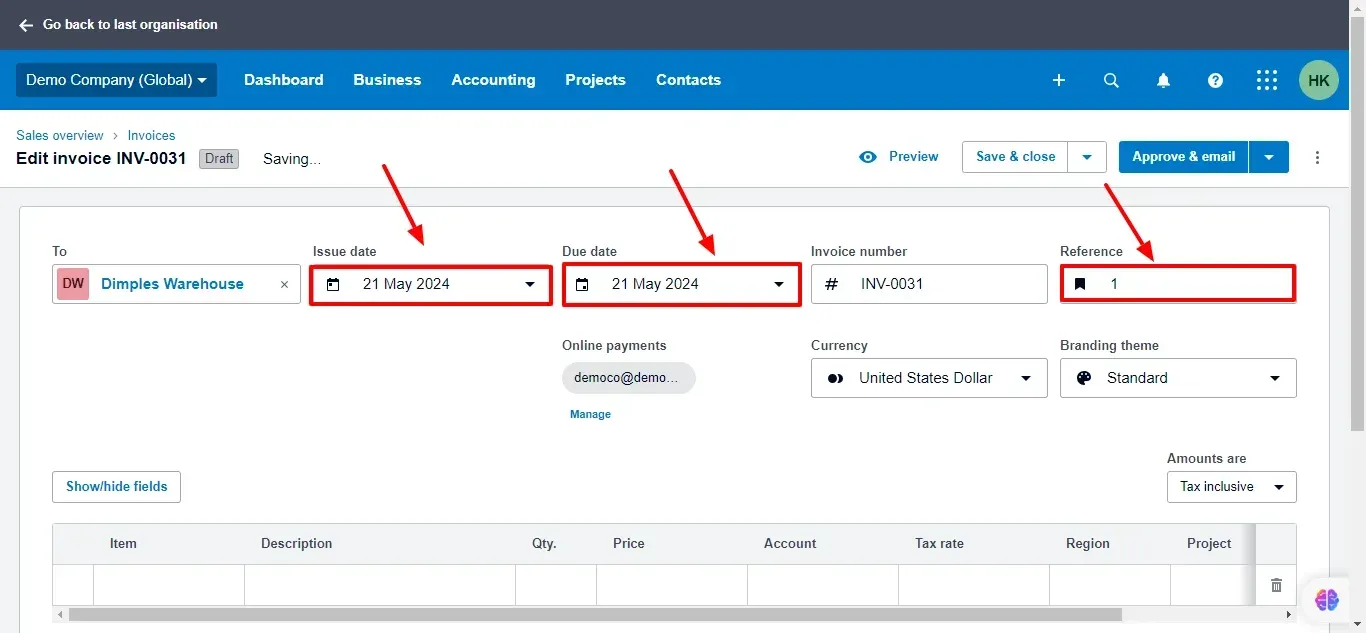
4. Fill in Invoice Details:
Enter the date in the Issue Date box (typically when you issue the invoice).
Set the Due Date (the date by which you expect payment).
You can optionally add a reference number for tracking purposes.
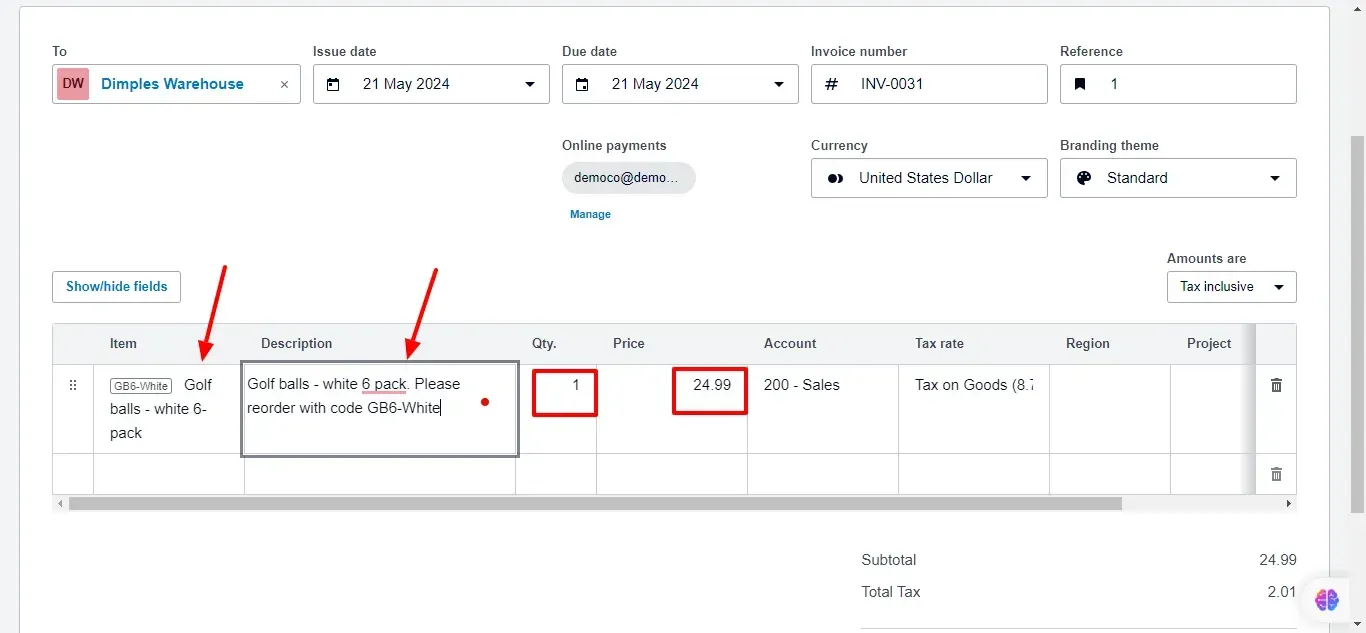
5. Itemize Your Products or Services:
In the invoice item list, you can:
Select existing products or services from the dropdown menu.
Click Add Item to create a new product or service.
Enter a clear Description for each item.
Specify the Quantity sold.
Enter the Unit Price for each item.
Xero will automatically calculate the Total amount (quantity x unit price).
6. Preview Invoice:
Click on Preview at the top to see how your invoice will look when you send it to your customer.
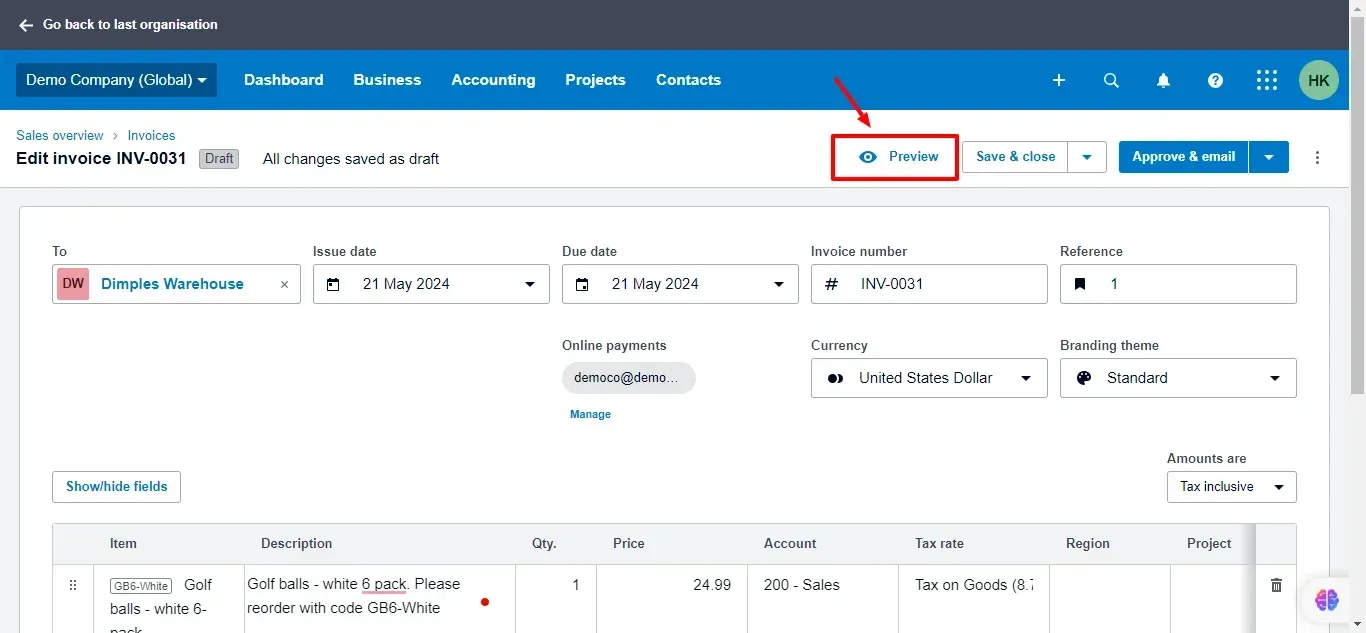
Here is how the invoice would look: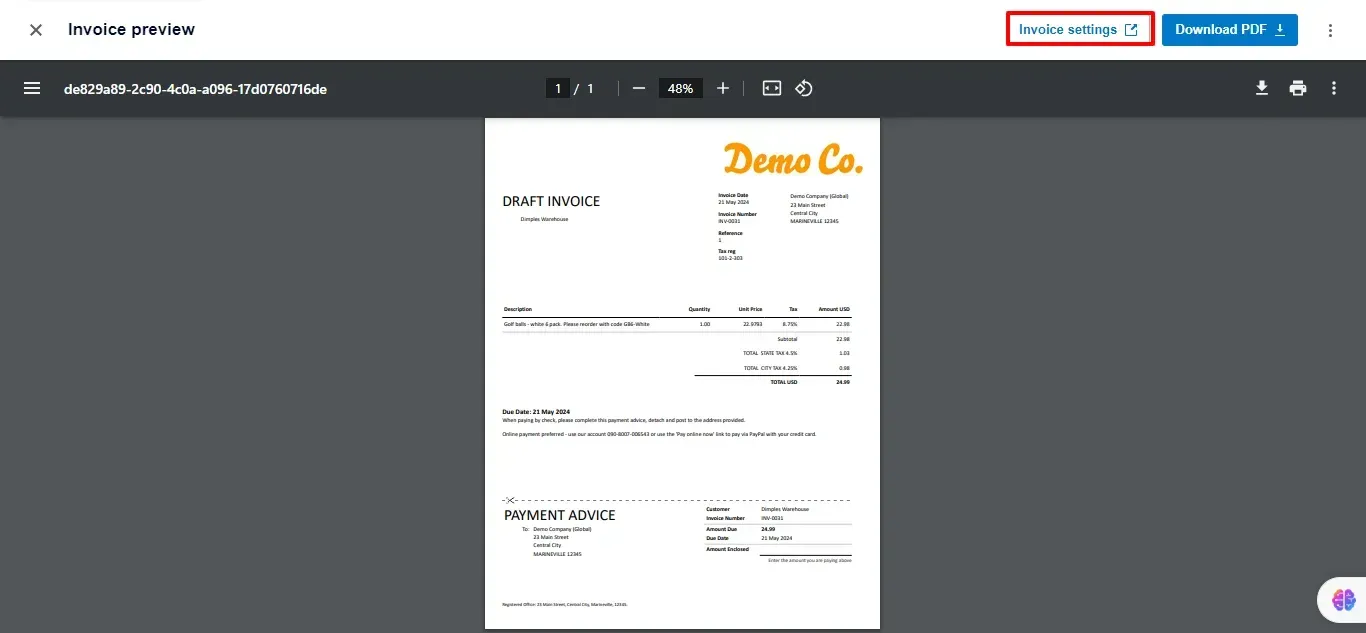
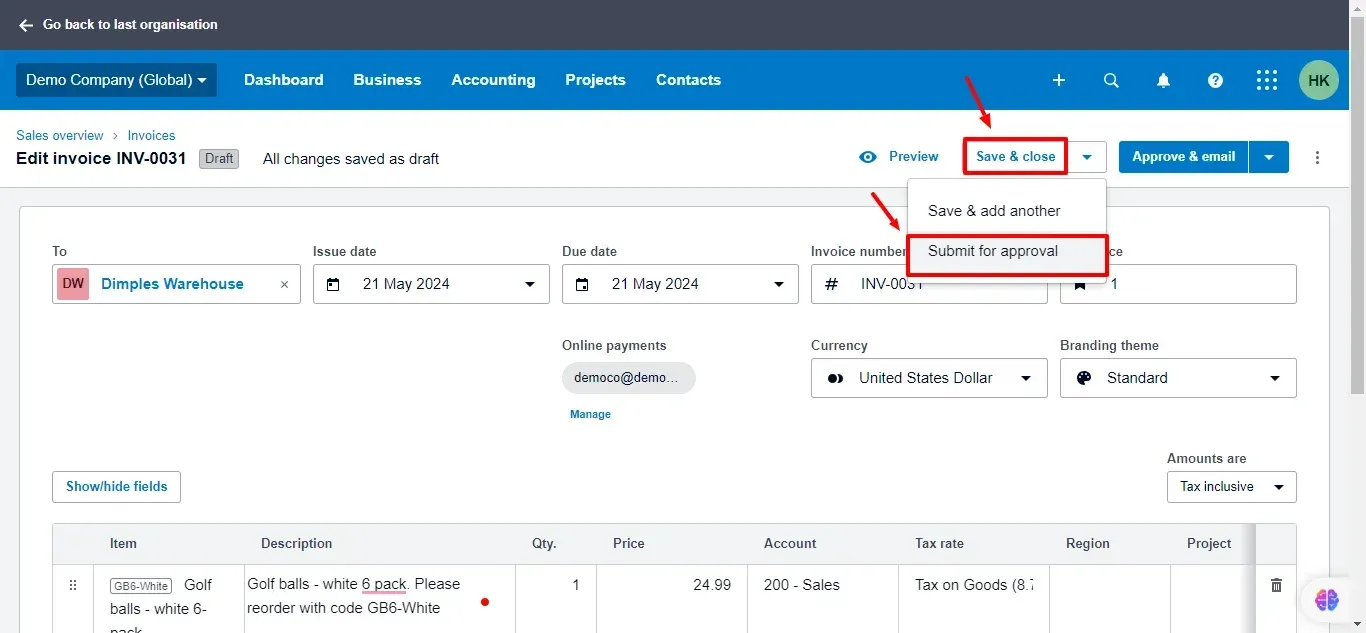
7. Save and Send the Invoice:
Once you've reviewed the invoice details, click Save & close.
You'll then have the option to Save & add another or Submit for approval.
Tracking and Managing Invoices
Invoice Dashboard: Use the dashboard to view all outstanding, paid, and overdue invoices at a glance.
Automated Reminders: Set up automatic reminders to prompt customers about upcoming or overdue payments.
Record Payments: Log payments as they come in, with Xero automatically updating the invoice status.
Reporting
Invoice and Debtor Reports: Generate reports like the Aged Receivables report to see who owes you money and how much.
Cash Flow Management: Utilize these reports to manage cash flow effectively, ensuring timely collections and financial stability.
Important Questions on Invoices
What is an Open Invoice?
An open invoice is an invoice that has been issued but not yet paid by the buyer. It remains "open" until payment is received.
What is an Outstanding Invoice?
An outstanding invoice has passed its due date and remains unpaid. It represents money owed to the seller that still needs to be collected.
What is an Electronic Invoice?
An electronic invoice (e-invoice) is a digital version of a paper invoice, often sent via email or electronic invoicing systems. It streamlines the billing process and reduces paperwork.
What is an Insurance Invoice?
An insurance invoice is a document issued by an insurance company detailing the premiums due for coverage. It includes policy details and payment terms.
What is an Invoice in Accounting?
In accounting, an invoice is a crucial document for recording sales, tracking receivables, and managing cash flow. It provides essential information for financial reporting and auditing.
What is an Invoice in QuickBooks?
In QuickBooks, an invoice is a document created within the software to bill customers for goods or services. It integrates with other financial data to streamline accounting processes.
What is an Acceptable Late Fee for an Invoice?
An acceptable late fee for an invoice varies by industry and agreement but typically ranges from 1.5% to 5% of the monthly overdue amount.
What are the Payment Terms for an Invoice?
Payment terms on an invoice specify when the payment is due and any applicable discounts or late fees. Common terms include Net 30, Net 60, or 2/10 Net 30.
What is VAT on an Invoice?
VAT (Value Added Tax) on an invoice is the amount of tax added to the sale price of goods or services, calculated as a percentage of the sale price.
What is an Invoice Template?
An invoice template is a pre-formatted document that includes all necessary invoice components. It can be customized to fit a business's specific needs and branding.
Important Questions on Industry-Specific Invoices
What is an Invoice on Amazon?
An Amazon invoice is a document sellers issue to buyers detailing the products sold, prices, and payment terms. It is used for billing and record-keeping purposes on the Amazon platform.
What is an Invoice on PayPal?
An invoice on PayPal is a digital invoice created and sent through the PayPal platform. It allows sellers to request payments and buyers to pay securely online.
What is an Invoice in Construction?
An invoice in construction is a document issued by contractors or suppliers to clients detailing the materials, labor, and services provided. It includes specific information related to construction projects.
What is an Invoice for a Package?
An invoice for a package is a document accompanying a shipment and details the contents, prices, and terms of the sale. It is used for billing and customs purposes.
What is an Invoice on eBay?
An eBay invoice is a document sellers issue to buyers detailing the items sold, prices, and payment terms. It is used for billing and record-keeping on the eBay platform.
Comparing Invoices: Invoices vs. Other Documents
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Purchase Order?
An invoice is a request for payment issued by the seller after providing goods or services. A purchase order (PO) is a document the buyer issues to authorize the purchase before the transaction occurs.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Receipt?
An invoice is a request for payment issued by the seller. A receipt is proof of payment issued by the seller after receiving the payment.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Bill?
Although invoices and bills are often used interchangeably, invoices are typically used in business-to-business transactions, while bills are commonly used in consumer transactions.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Statement?
An invoice details a specific transaction and requests payment. A statement summarizes all transactions between the buyer and seller over a period, showing outstanding balances and payments made.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Sales Receipt?
An invoice requests payment after a sale, while a sales receipt is issued at the time of purchase to acknowledge immediate payment.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and an Estimate?
An invoice requests payment for goods or services provided. An estimate gives an approximate cost for potential goods or services before the transaction occurs.
What is the Difference Between an Invoice and a Quote?
An invoice requests payment after goods or services are provided. A quote provides a detailed price offer for specific goods or services before the sale.
What is the Difference Between a Commercial Invoice and a Standard Invoice?
A commercial invoice details goods shipped across borders for international trade, while a standard invoice is used for domestic transactions.
What is the Difference Between a Proforma Invoice and a Regular Invoice?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary bill of sale sent to buyers before goods or services are delivered, giving an estimate of costs. A standard invoice is issued after delivery, requesting payment.
Consequences of Missing Out Invoice Payments
What is an Overdue Invoice?
An overdue invoice is an invoice that has yet to be paid by the due date specified in the payment terms.
What Happens if an Invoice is Incorrect?
If an invoice needs to be corrected, it should be amended or reissued with the correct details.
What Happens if an Invoice is Not Paid?
If an invoice is not paid, the seller may send reminders, charge late fees, or escalate the matter to a collections agency. It’s crucial to address unpaid invoices promptly to maintain cash flow.
What is an Unpaid Invoice?
An unpaid invoice is an invoice that has been issued but is yet to be paid by the buyer. It remains in the seller’s accounts receivable until payment is received.
What is an Interim Invoice?
An interim invoice is a partial invoice issued during a project or contract period, covering a portion of the total cost. It helps manage cash flow and ensures that payments are made in stages.
What is an Invoice Remittance?
An invoice remittance is a document the buyer sends to the seller confirming payment and specifying which invoices the fee applies to.
Automation in Invoice Management
What is an Automated Invoice?
Invoicing software generates and sends an automated invoice, reducing manual effort and ensuring timely billing.
What is an EDI Invoice?
An EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) invoice is a standardized electronic document used to digitally exchange invoice information between businesses, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
What is Invoice Approval?
Invoice approval involves reviewing and approving invoices before they are paid. This process ensures accuracy and compliance with internal policies.
What is an Invoice System?
An invoice system is software designed to create, send, and manage invoices. It helps automate the invoicing process and integrates with other financial systems for seamless operation.
Managing Invoices in eCommerce
In eCommerce, managing invoices efficiently is crucial for seamless transactions and customer satisfaction. Here’s how to handle invoices in an eCommerce environment:
Generating Invoices
Integrated Invoicing Tools: Use the invoicing tools integrated into your eCommerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce).
Order Confirmation: Automatically generate and send an invoice detailing all order information when a customer places an order.
Customizing Invoices: Tailor invoice templates to include your branding, terms, and conditions.
Tracking and Managing Invoices
Order Management System: Leverage your order management system to track all invoices and their statuses.
Payment Gateways: Link payment gateways to your invoicing system for automatic updates on payment status.
Follow-up and Reminders: Set up automated follow-ups and reminders for unpaid or overdue invoices.
Streamline Payments with PayTraQer: To efficiently manage payment tracking and reconciliation, use PayTraQer to automate and streamline bookkeeping processes. This ensures accurate updates and saves valuable time. Try PayTraQer to organize your online payment and sales data today.
Reporting
Sales Reports: Create sales reports to monitor revenue, track unpaid invoices, and analyze customer payment behaviors.
Inventory and Sales Integration: Integrate your invoicing system with inventory management to maintain accurate stock levels and streamline order fulfillment.
Financial and Legal Aspects of Invoices
What is an Invoice Finance Facility?
An invoice finance facility allows businesses to borrow money against their outstanding invoices. It provides immediate access to funds, helping improve cash flow.
What is the Impact of Receiving an Invoice for Inventory Purchased?
Receiving an invoice for inventory purchased impacts the accounts payable and inventory accounts. It increases the inventory value on the balance sheet and records a liability in accounts payable.
What is the Best Way to Create an Invoice?
The best way to create an invoice is to use invoicing software that ensures accuracy, compliance, and professional presentation. Customize the template to include all necessary details and branding elements.
What is Legally Required on an Invoice?
Legally required elements on an invoice vary by country but generally include:
Seller and buyer contact information
Invoice number and date
Description of goods or services
Prices and quantities
Payment terms
Applicable taxes
Total amount due
What Documentation or Information is Needed to Process an Invoice for a New Vendor?
To process an invoice for a new vendor, you typically need:
Vendor's contact information and tax identification number
Purchase order (if applicable)
Contract or agreement details
Description of goods or services
Pricing and payment terms
What is the Correct Way to Write Off an Old Invoice from a Closed Prior Year?
To write off an old invoice from a closed prior year, you need to:
Record a credit note for the outstanding amount
Adjust the accounts receivable balance
Update financial statements to reflect the write-off
Ensure compliance with accounting standards and tax regulations
What is an Invoice Register?
An invoice register is a record of all invoices issued and received. It is used for tracking and managing accounts payable and receivable, helping ensure accurate financial reporting and cash flow management.
International Considerations for Invoicing
Tax Implications
VAT/GST:
Depending on the destination country and the value of the goods or services, a value-added tax (VAT) or a goods and services tax (GST) may apply.
Indicate VAT/GST rates and any applicable exemptions on your invoice.
Research tax treaties between your country and the client's country to determine who is responsible for withholding taxes. This can get complex, so it is recommended that you consult a tax professional.
Reverse Charge Mechanism:
In some cases, the reverse charge mechanism applies in EU transactions. This means the seller's responsibility to pay VAT shifts to the buyer.
Understanding reverse charge rules is crucial to avoid VAT miscalculations.
Withholding Taxes:
Certain countries require withholding taxes on payments made to foreign businesses.
The withholding tax rate varies by country and type of service.
Research withholding tax requirements to ensure proper tax compliance.
Customs Requirements
HS Tariff Codes:
The Harmonized System (HS) classification system assigns a unique code to identify goods for customs purposes.
Including the correct HS tariff code on your commercial invoice facilitates a smooth customs clearance process.
Certificates of Origin:
Certain countries may require a certificate of origin, a document verifying the goods' country of manufacture.
Chambers of Commerce or other designated authorities typically issue certificates of origin.
Payment Methods
Letters of Credit:
Letters of credit offer a secure payment method for international transactions.
A bank guarantees payment to the seller upon meeting specific conditions outlined in the letter of credit.
International Payment Gateways:
International payment gateways allow secure online transactions in various currencies.
These services often come with lower fees compared to traditional wire transfers.
Security Considerations for Invoicing
Data Security:
Encrypting invoice data during transmission and storage protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Implement strong password protocols and access controls for invoicing software.
Risk of Fraud:
Be cautious of fake invoices with spoofed sender addresses or incorrect bank details.
Verify the recipient's information and confirm any changes in payment instructions directly with the client.
Advanced Features in Invoicing Software
Integration with Accounting Systems:
Seamless integration with accounting software automates data entry and reduces errors.
This streamlines tasks like recording sales, managing accounts receivable, and generating financial reports.
Recurring Invoices and Subscriptions:
Automate the creation and delivery of invoices for recurring services or subscriptions.
This saves time and ensures clients receive invoices on schedule.
Online Payment Processing:
Integrate online payment gateways directly into your invoicing software.
This allows clients to pay invoices securely and conveniently, accelerating payment collection.
Project Management and Time Tracking Features:
Some invoicing software offers project management and time-tracking features.
These tools help track billable hours and create invoices based on project milestones.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of invoicing is fundamental to maintaining a healthy financial flow in any business. From understanding the pivotal role of invoices in facilitating transactions to delving into the nuances of managing them efficiently in platforms like QuickBooks and Xero, this guide has provided a comprehensive roadmap for businesses of all sizes. By leveraging the insights shared here, companies can streamline invoicing processes, ensure timely payments, and confidently navigate potential challenges. Effective invoicing practices contribute significantly to financial stability, client relationships, and business success.
Recommended reading:
FAQs
How do you handle disputes over invoice amounts?
When faced with a dispute over an invoice amount, it's crucial to approach the situation calmly and professionally. Start by reviewing the invoice details and comparing them with the agreed-upon terms of the project or service. If there are discrepancies, communicate with the client promptly and provide clear documentation supporting your position. Aim to resolve the issue amicably through negotiation and compromise, keeping the client relationship in mind.
What should you do if a client consistently pays late?
Late payments consistently can disrupt your cash flow and affect your business operations. Begin with polite but firm reminders to the client about their overdue invoices. If the problem persists, consider implementing late payment fees per your contract terms. Additionally, have open discussions with the client to understand any underlying issues causing the delays and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
How to apply for early payment discounts?
To apply for early payment discounts, first review your vendor or supplier agreements to understand if they offer such incentives. If early payment discounts are available, ensure you meet the criteria, such as making payments within a specified timeframe. Communicate with your vendors proactively, expressing interest in availing of early payment discounts, and inquire about any necessary steps or forms to complete the process smoothly.
Are invoicing and accounts receivable the same thing?
Yes, invoicing and accounts receivable are closely related concepts that focus on managing what is owed to you. While some may view invoicing merely as sending bills, it encompasses a broader process. This process starts when you establish payment terms with a customer and continues until payment is received. There are often several steps involved in this cycle.
What is the difference between an invoice and a receipt?
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to request payment for goods or services provided, detailing the amount due. On the other hand, a receipt is issued after payment is received, serving as proof that the payment has been made.
How can I automate the invoicing process?
Accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero can automate the invoicing process. These platforms allow you to create recurring invoices, schedule automatic reminders for due payments, and integrate with payment gateways to update payment statuses automatically.
What should be included in an invoice?
An invoice should include the following details:
Seller’s information (name, address, contact information)
Buyer’s information (name, address, contact information)
Invoice number
Invoice date
List of items or services provided
Prices and quantities
Payment terms
Total amount due
Any applicable taxes or discounts
How do I handle unpaid invoices?
If an invoice remains unpaid past the due date, follow these steps:
Send a friendly reminder email or call the client.
Issue a formal reminder with the invoice attached.
Consider implementing late payment fees as per your contract.
Negotiate a payment plan if the client is facing financial difficulties.
As a last resort, engage a collections agency to recover the outstanding amount.